In today’s data-driven organizations, managing information is no longer optional, it’s critical to survival. But not all data is equal.
Some data powers the entire enterprise, while some data drives what your customers actually see. This is where Master Data Management (MDM) and Product Information Management (PIM) come in.
Think of it this way: MDM is the brain of the enterprise, keeping all critical information accurate, consistent, and trusted.
PIM is the voice of the enterprise, making sure your product content is clear, enriched, and ready to engage customers wherever they shop.
What Problems Do MDM and PIM Solve?
MDM – The Backbone
MDM solves a very specific problem: how to create a single source of truth across an entire organization.
Without MDM, organizations often struggle with:
Duplicate or conflicting materials, customer, or, product data
Inaccurate reporting and analytics
Compliance and regulatory risks
Operational inefficiencies due to inconsistent data across departments
For example, imagine a global manufacturing company tracking suppliers, warehouses, and customers across multiple ERPs.
Without MDM, a single supplier could appear three times with slightly different names, leading to duplicate payments, delayed shipments, or wrong material allocations.
MDM centralizes all critical data, validates it, cleans it, and distributes it to downstream systems so everyone, from finance to operations, speaks the same language.
PIM – The Frontline
While MDM governs the enterprise, PIM governs product content for sales and marketing.
Without PIM:
Product catalogs may be inconsistent across e-commerce, marketplaces, and stores
Missing images, wrong descriptions, or incorrect prices frustrate customers
Marketing teams spend hours manually copying content into multiple platforms
PIM centralizes all product-related information, attributes, images, descriptions, videos, certifications, and ensures channel readiness.
It’s the system that ensures your Amazon page, Shopify store, and retail POS all say the same thing about your products.
Key Differences: MDM vs. PIM
| Feature | Master Data Management (MDM) | Product Information Management (PIM) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enterprise-wide data consistency, compliance, and golden records | Accurate, enriched, and customer-ready product content |
| Scope | Multi-domain: Product, Supplier, Customer, Service, Materials, Location, Finance | Product-focused: SKUs, Attributes, Media, Descriptions |
| Primary Users | IT, Data Stewards, Data Analysts, Data Scientists | Marketing, E-commerce, Product Content Managers |
| Focus | Accuracy, 360° view, operational efficiency | Speed-to-market, conversion, channel consistency |
| Triggers | Data duplication, regulatory mandates, operational inconsistencies | Catalog expansion, new sales channels, product updates |
| Integration | ERP, CRM, BI, Analytics | E-commerce platforms, CMS, Marketplaces, DAM |
| Objective | Enterprise-oriented governance and compliance | Strategical approach to sales/marketing of products |
| Teams Owning | IT Technical Team, Operational Data Stewards, Domain Experts | Marketing, Product Content Managers, E-commerce Teams |
How They Work?
MDM
PIM
Imagine a company wants a 360° view of its suppliers.
Step 1: Create
- Raw supplier data comes from multiple ERPs, procurement systems, and spreadsheets.
- Duplicate entries are flagged and cleaned.
Automated data enrichment enhances this data by pulling relevant information from trusted external sources, such as supplier ratings, financial health metrics, or regulatory compliance data.
Step 2: Match & Merge
The system identifies that “Acme Ltd.”, “Acme Ltd Inc.”, and “ACME Corporation” are the same entity.
A single golden record is created.
Master data cleansing and standardization in MDM ensures that downstream systems consume a single golden record instead of fragmented, duplicate entities.
Step 3: Approve
- Data Stewards review and validate the record.
Step 4: Distribute
- This verified supplier record is sent to procurement, finance, logistics, and analytics systems.
Why it matters: When the next purchase order is issued, the system ensures the right supplier is paid, the invoice matches, and reporting is accurate across all departments.
Let’s follow a product from concept to customer touchpoint:
Step 1: Import & Enrich
- Product data (SKU, specs, images) is imported from ERP or supplier catalogs.
- Marketing adds enriched descriptions, videos, and localization.
Step 2: Validation & Channel Readiness
- Completeness rules ensure no product is missing required attributes.
- Channel-specific formatting ensures the same product looks perfect on Amazon, Shopify, and the company website.
Step 3: Syndication
- Data is pushed to multiple sales channels in real time.
- Customers see accurate, rich content that reduces returns and increases conversions.
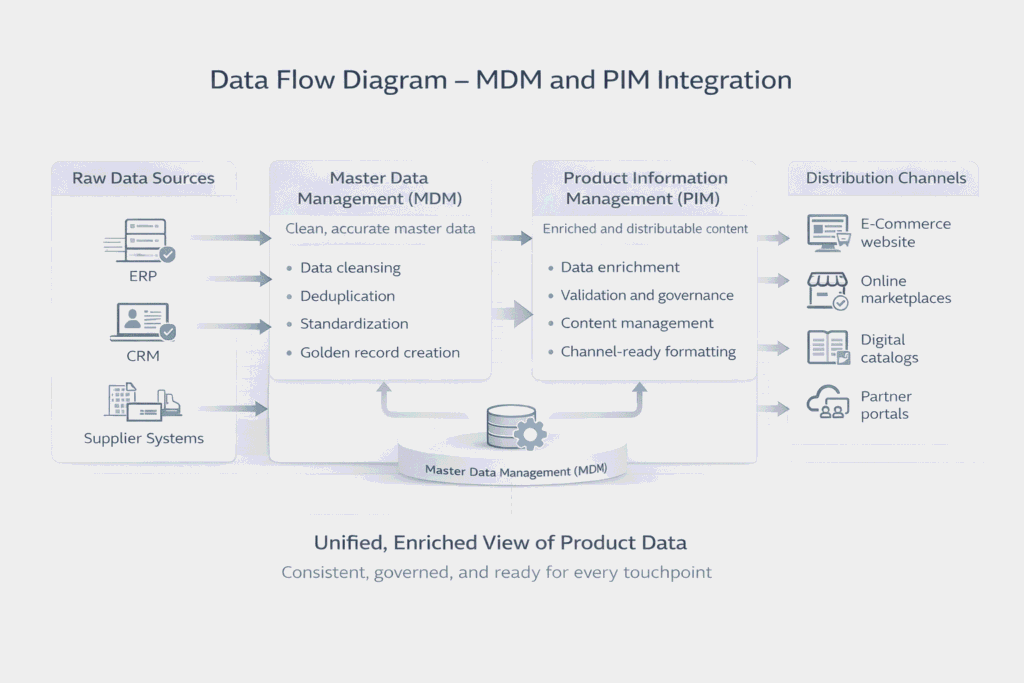
MDM + PIM in Tandem – A Real-World Scenario
Imagine a global electronics company launching a new smart thermostat:
MDM cleans the data:
- Ensures the product, suppliers, and manufacturing plants are accurately recorded.
- Verifies compliance, tax codes, and financial mappings.
PIM enriches the product content:
- Adds images, manuals, features, multilingual descriptions.
- Prepares content for Amazon, physical stores, and regional websites.
Outcome:
- Internal systems have accurate operational data.
- Customers see consistent, engaging product content across all channels.
Teams Owning and Managing MDM and PIM
MDM Ownership
- IT Technical Team: Implements and maintains the MDM tools and infrastructure to build the systems that own master data, managing technological aspects like security and integration.
- Domain Experts: Have ultimate authority and accountability for specific data domains to define purpose of the data, strategic vision, and adopt policies within their domain.
- Operational Data Stewards: Business focused individuals who manage data and resolve issues to meets business needs. Act as the key bridge between business and IT to ensuring data trustworthy data.
PIM Ownership
- Marketing Teams: They are primary users, utilizing PIM to create product shopping experiences, manage digital assets, and structure the content for varied campaigns.
- E-commerce Teams: These teams rely mostly on PIM to ensure accurate up-to-date product data on all e-commerce websites and market zones to drive sales ratio and reduce return rates.
- Product Content Managers: These specialists manage the routine data, localization, and quality approvals within the PIM system.
- Sales Teams: They use PIM to quickly access accurate product information and materials for customer interactions and sales support.
PIM & MDM Use Cases Across Different Industries
| Industry | MDM Use Cases | PIM Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Retail & E-Commerce | Single product/customer view across stores and ERP | Product catalog management, channel syndication |
| Manufacturing | Supplier and material data governance | Product specifications and marketing content |
| Healthcare | Patient and supplier data compliance | Product instructions, regulatory content |
| Finance | Customer 360°, compliance reporting | N/A |
| Distribution & Wholesale | Vendor/customer/product data for supply chain | Multichannel product catalogs |
MDM & PIM Data Lifecycle Engineering
MDM and PIM operate in parallel, but their technical workflows differ:
| Lifecycle Stage | MDM Action | PIM Action | Technical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | Pulls data from ERP, CRM, legacy systems | Pulls base product info from MDM | ETL/ELT pipelines, API connectors |
| Cleansing & Validation | Deduplication, normalization, validation rules | Completeness checks, attribute validation | Rule engine, ML anomaly detection |
| Enrichment | Add classifications, supplier info, pricing data | Add descriptions, images, SEO metadata | AI/NLP for copy, DAM integration for media |
| Approval & Governance | Workflow approvals, exception handling, survivorship rules | Channel release approvals, localization approvals | Role-based access control, BPM workflows |
| Syndication | Publish golden record to ERP, BI, analytics | Export to e-commerce, marketplaces, CMS | API feed, format transformation (JSON, XML, CSV) |
| Feedback & Analytics | Data quality dashboards, exceptions, reconciliation | Conversion, catalog completeness, campaign metrics | BI dashboards, ML insights, feedback loops |
Scenario: Launching 50,000 new SKUs for winter season
| Stage | Real-World Event | MDM Action | PIM Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| SKU Creation | Supplier submits catalog | MDM deduplicates, validates master SKU, assigns global identifier | Base SKU pulled into PIM |
| Enrichment | Marketing creates campaigns | MDM ensures consistent pricing and category | PIM adds images, videos, descriptions, SEO metadata |
| Channel Syndication | Publish to Amazon, Shopify, website | ERP receives golden SKU | PIM transforms data to channel-specific formats |
| Feedback | Conversion & click data collected | MDM reconciles supplier and ERP updates | PIM flags missing content or underperforming SKUs |
When to Implement Both MDM and PIM in Tandem?
1. Urgent e-commerce demands and adverse systemic data issues: A parallel approach allows to achieve faster wins with PIM in customer-facing channels while MDM focuses on the foundational, plant-wise data inconsistencies.
2. Industries like manufacturing, retail, pharmaceuticals, or finance often require MDM for strict governance and compliance across all data domains (customer, product, supplier etc.), while PIM is used for managing public-facing product specs and marketing content.
3. MDM can govern internal supply chain data and give a comprehensive safe journey, while PIM ensures the product content is accurate and enriched.
This optimised and linked data flow provides a complete picture for good decision-making and arriving quicker end results.
4. Pursuing a complex global digital transformation or scaling: Rapid growth creates data complexities on multiple fronts.
Using both PIM and MDM systems provide the necessary foundation for upgraded initiatives like AI-driven recommendations across global markets and multiple sales channels.
5. Leveraging AI for both customer experience and internal efficiency: MDM provides the reliable, accurate and clean data foundation required to train AI models for internal analytics, while PIM uses AI for automated content enrichment, smart tagging, and localization to improve the customer experience.
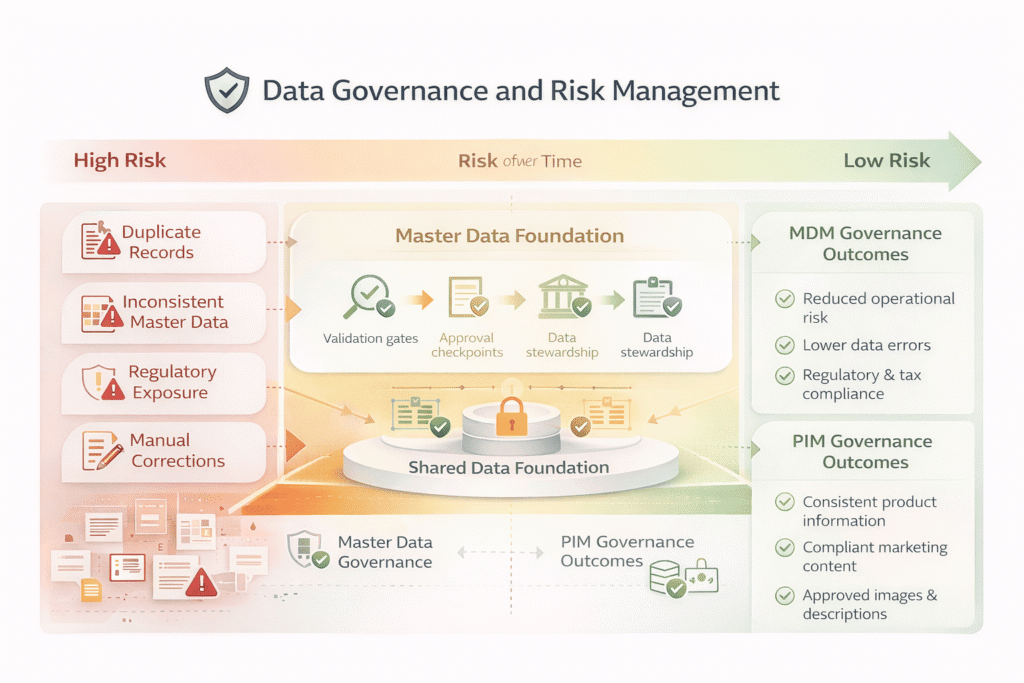
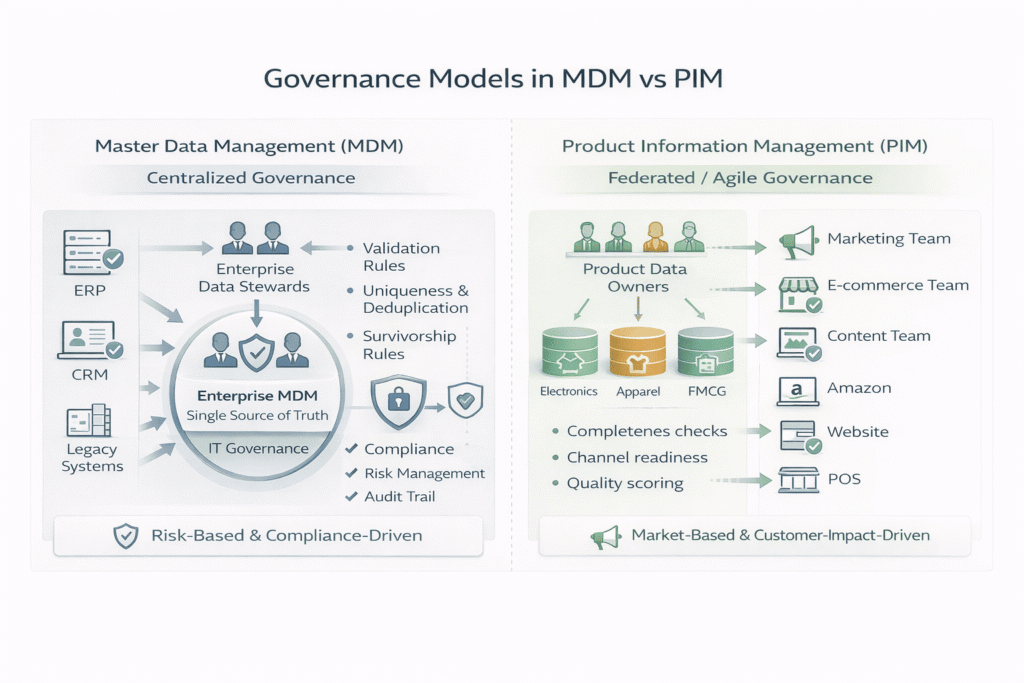
Governance Models: Centralized vs Federated
Data Stewardship Boundaries
- Enterprise data stewards (MDM): Enterprise Data Stewards in MDM are the crucial business experts who govern and manage the entire quality of an organization’s master data (like product, customer, asset info) by resolving issues, bridging business& IT, and bringing policies to create trusted data.
- Domain or product data owners (PIM): A product data owner is an individual or team responsible for the completeness, accuracy, governance, and enrichment of a specific category or domain of product data within the organization.
Why governance escalation paths differ?
MDM involves enterprise IT-led governance with cross-functional escalation, while PIM focuses on product related, marketing/business-led data enrichment with more agile workflows.
Policy Enforcement vs Editorial Control
MDM enforces:
1. Validation Rules: These are a set of data rules that check the completeness, as it is processed. Validation rules enforce standard formats that ensure critical fields are not left blank, or verify data against external sources, to prevent junk data.
2. Uniqueness: MDM ensures that each item has a unique identifier and prevents duplicate records in system. This includes using techniques like fuzzy matching to find out records that identifies the similar entity, even if the data contains slight errors.
3. Survivorship: When the MDM system identifies duplicate data from different sources for the same item, rules will determine which data values should be retained to populate the master record.
PIM enforces:
1. Completeness: PIM systems use strong validation rules to assure that all mandatory attributes are present before a product can be launched. This prevents products with missing formation (e.g., key specification) from reaching the customer touchpoints.
2. Channel Readiness: PIM helps businesses format product information for the unique requisites of various channels (e.g., marketplaces like Amazon, E Commerce websites.
3. Quality Scoring: Advanced PIM solutions generate complete reports that highlight data inconsistencies. These measures help to prior fix data issues, assuring information is consistent.
Approval Workflows: Risk-Based vs Market-Based
MDM approvals driven by compliance and downstream risk:
- MDM overcomes conflicts across different plants and departments. This proactive management of data stands as single source of truth for explaining consistent adherence to regulations across the entire organization. MDM simplifies and supports compliance and drives efficiency.
- Consistent data prevents issues like lagging in product promotions or supply chain controversies that contribute to poor data quality.
PIM approvals are driven by brand consistency and customer impact:
Brand Consistency:
- Only Centralized Digital Assets with PIM will ensure that branded logos and images are used across all touchpoints.
- Maintaining Channel Specific Guidelines with PIM allows accurate and consistent content to be adapted for specified audiences of varied platforms.
- PIM insists on standardized descriptions, and messaging, thereby avoiding the brand promotion from becoming diluted across team members and channels.
Customer Impact
- Enriched product data allows for personalized shopping experience reducing post-purchase issues and uncertainty.
- PIM approvals ensure customers to receive reliable and complete product information as incomplete data will lead to customer complaint lowering their satisfaction.
- Consistent experiences across in-store channels build customer trust in the brand’s reliability.
AI & Automation in MDM/PIM
Modern MDM/PIM platforms increasingly integrate AI and automation:
MDM: Predictive data quality alerts, anomaly detection, automated deduplication, classification suggestions.
PIM: Automated content enrichment (NLP for descriptions), smart image tagging, localization using ML.
Integrated Impact: Reduces manual interventions, accelerates SKU launches, ensures compliance, improves analytics.
Business Impact & KPIs
| Metric | MDM Impact | PIM Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | 15–25% reduction in operational costs (Source) | 6× faster product data management (Source) |
| Error Reduction | 40–60% fewer duplicates/errors | 20–50% higher conversion due to accurate content |
| Inventory & Supply Chain | 10–20% reduction in stock inconsistencies | SKU syndication reduces out-of-stock events |
| Time-to-Market | Faster product launch cycles (2×) | Faster enrichment & syndication to channels |
| Compliance | 50–70% fewer data-related regulatory issues | Ensures marketing/legal compliance in product content |
MDM and PIM, though distinct in their focus, work together to provide a robust data foundation for modern organizations.
MDM ensures that the core business data is accurate, consistent, and reliable across the enterprise, while PIM delivers enriched, customer-ready product information that drives better engagement and conversions.
The combination of these systems, enhanced by features like automated enrichment and master data cleansing, empowers businesses to streamline operations, improve customer experiences, and stay ahead of market demands.
By aligning both, organizations can not only maintain data integrity but also maximize their efficiency and adaptability in a rapidly changing digital world.





