Manufacturing Master Data Management serves as the foundational infrastructure for operational excellence, enabling organizations to transform fragmented data silos into a unified source of truth.
Despite significant investments in advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and automation, manufacturers continue to grapple with fundamental data quality issues that undermine operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.
A study across enterprise environments reports that companies often manage data across 17 different enterprise systems, with 72% struggling to integrate legacy data, contributing to quality issues and long delays in transformation efforts
When properly managed and integrated, master data becomes the single source of truth that empowers manufacturers to optimize production workflows, streamline supply chains, maintain regulatory compliance, and deliver superior customer experiences through data-driven decision-making.
Key Stakeholders of Manufacturing MDM
Different organizational functions depend on reliable master data to execute their responsibilities effectively.
Accurate BOMs and material data enable realistic schedules, timely material ordering, and reduced downtime.
Standardized supplier and material data improves sourcing, spend control, and supplier performance management.
Reliable asset and equipment data supports predictive maintenance, spare parts optimization, and higher uptime.
Consistent product and supplier data ensures compliance, traceability, and effective corrective actions.
Clean master data enables accurate reporting, budgeting, costing, and profitability analysis.
MDM ownership, data standards enforcement, system integration, and enterprise-wide governance.
Industries That Depend on Manufacturing MDM
Manufacturing Process Challenges Traceable to Master Data Issues
In most manufacturing environments, unexpected equipment failures often expose deeper master data issues lurking in the background.
When a critical asset fails, maintenance discovers multiple part numbers for the same component.
Item descriptions vary – some too generic, others incomplete, and rarely aligned with actual supplier catalogs.
Procurement teams struggle to identify the correct part or supplier, leading to confusion and sourcing delays.
Common Data Challenges:
Incomplete or missing data: Critical attributes – dimensions, material compositions, or supplier codes – often absent.
Non-standardized naming conventions: Similar components recorded differently across systems.
Duplicate records: Multiple item codes for the same part, confusing maintenance and procurement teams.
Outdated or unverified information: Supplier details, pricing, or technical specs not regularly validated.
Poor catalog alignment: Internal data rarely match supplier or OEM catalogs.

Consequences:
Sourcing delays due to mismatched or duplicated data.
Prolonged equipment downtime as teams sift through inconsistent records.
Idle production lines, rising costs, and lost revenue opportunities.
Difficulty in identifying the correct part or approved supplier.
In short, data inconsistency silently erodes operational efficiency and exposes how dependent manufacturing performance is on reliable, standardized master data.
Why is this a Recurring Issue?
Most large enterprises run on a patchwork of systems that each maintain a different “truth” about the same asset.
ERP systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle): Handle finance and materials.
Procurement platforms (e.g., Ariba, Coupa): Manage sourcing activities.
Maintenance systems (e.g., Maximo, SAP PM): Track asset performance.
Additional tools such as a CMMS or Work Order systems may also feed data directly into the ERP/EAM layer.
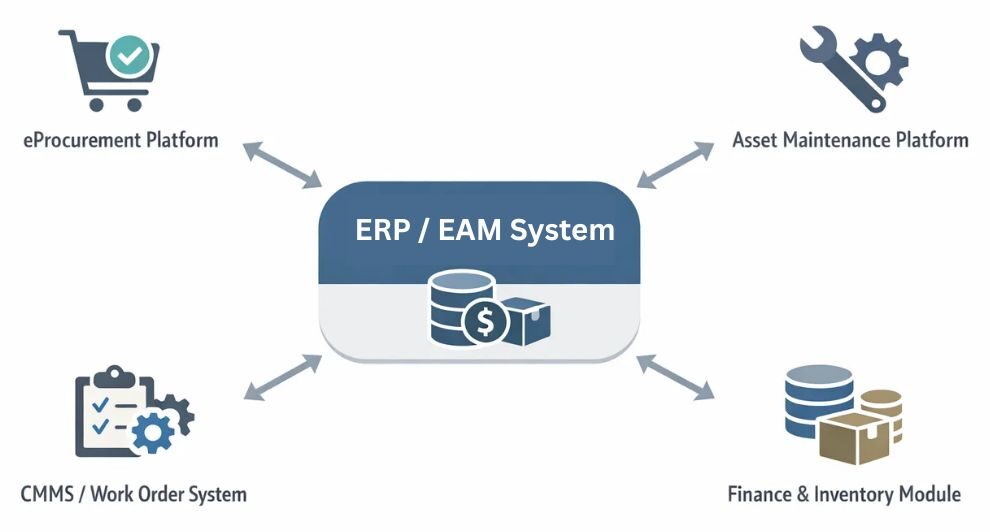
The challenge:
Each system stores its own version of the same part:
Different naming conventions.
Missing or inconsistent specifications.
Varied supplier records.
Operational impact:
Procurement searches one database, maintenance updates another, and quality verifies a third.
Finance then attempts to reconcile these inconsistencies to determine inventory value.
The outcome: the organization functions like three separate companies pretending to be one, generating waste at every touchpoint.
To function as a truly integrated enterprise, manufacturers must manage and synchronize master data for all critical domains: materials, services, assets, products, suppliers, and employees.
Benefits of Reliable, Standardized Master Data:
Establishes a single source of truth across all enterprise systems.
Eliminates rework and redundant validation efforts.
Streamlines sourcing, inventory, and maintenance workflows.
Enhances supply chain visibility and regulatory compliance.
Enables data-driven decision-making and optimized production performance.
When master data is clean, consistent, and connected, manufacturing operations shift from reactive firefighting to predictable, efficient performance.
Manufacturing Master Data Domains
Master Data Domains in manufacturing represent the foundational datasets that drive every business process, from procurement and production to maintenance, sales, and financial reporting.
Each domain defines a specific “source of truth” that keeps operations synchronized, efficient, and data-driven.
What it represents in manufacturing
Material Master Data defines everything the factory buys, stores, consumes, assembles, or sells-from raw materials and components to MRO spares and finished goods. It is the backbone for BOMs, inventory planning, procurement, costing, and maintenance.
Typical attributes
Part / Material number
Standardized description (naming convention)
Material type (Raw, Semi-finished, Finished, MRO)
Specifications (size, grade, tolerance)
Unit of Measure (EA, KG, MTR)
Approved suppliers
Cost and valuation class
Commodity codes (UNSPSC, eCl@ss)
Manufacturing example
Part Number: 6205-2RS1
Description: Bearing, Deep Groove Ball, Sealed
Material: Stainless Steel
Size: 25mm ID × 52mm OD
Supplier: SKF
UoM: Each
UNSPSC: 31161607
Why it matters on the shop floor
Prevents duplicate materials (same bearing created 5 different ways)
Enables accurate MRP and spare parts planning
Reduces excess inventory and emergency purchases
Ensures correct materials are issued to work orders and production orders
What it represents in manufacturing
Supplier Master Data captures who you buy from, under what terms, and how reliable they are. It is essential for strategic sourcing, compliance, MRO spend analysis, and risk management.
Typical attributes
Supplier ID and legal name
Contact and address details
Approved material categories
Quality and compliance certifications
Performance metrics (OTD, quality score)
Payment terms and contract validity
Manufacturing example
Supplier ID: 12345
Name: ABC Fasteners Pvt. Ltd.
Category: Industrial Fasteners
Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 14001
On-Time Delivery: 96%
Payment Terms: Net 45
Why it matters in manufacturing
Ensures only approved vendors are used for critical components
Enables supplier performance tracking and rationalization
Supports audits, compliance, and ESG reporting
Reduces procurement cycle time and maverick buying
What it represents in manufacturing
Customer Master Data stores all information about the customers who buy products, enabling accurate order processing, delivery, billing, and after-sales service. It connects sales, production, and supply chain for better customer experience.
Typical attributes
Customer ID and name
Contact and billing information
Shipping addresses and delivery preferences
Payment terms and credit limits
Industry and segment classification
Order history and service agreements
Manufacturing example
Customer ID: CUST-1001
Name: Global Petrochem Ltd.
Billing Address: 123 Industrial Park, Houston, TX
Shipping Address: Plant 3, Houston #2
Payment Terms: Net 30
Industry: Chemicals Manufacturing
Why it matters
Ensures accurate and timely order fulfillment
Links customer-specific requirements to production and inventory
Supports sales analytics, forecasting, and CRM initiatives
Reduces errors in billing, shipping, and after-sales service
What it represents in manufacturing
Asset Master Data defines machines, production lines, utilities, and critical infrastructure used to manufacture products. It is the foundation for maintenance planning, reliability engineering, and asset lifecycle management.
Typical attributes
Asset ID and hierarchy (Plant → Line → Machine)
Manufacturer, model, serial number
Installation and commissioning date
Location and operating context
Maintenance strategy (Preventive / Predictive)
Spare parts linkage
Manufacturing example
Asset ID: A-1423
Equipment: CNC Milling Machine
Manufacturer: Siemens
Model: PLC-X100
Location: Plant 3 – Line 2
Commissioned: 2019-04-12
Last Service: 2025-08-15
Why it matters
Enables preventive and predictive maintenance
Links correct spare parts to each asset
Reduces unplanned downtime and MTTR
Supports asset performance analysis (OEE, failure trends)
What it represents in manufacturing
Location Master Data defines where operations, inventory, and assets physically exist, from global plants to warehouse bins and maintenance zones.
Typical attributes
Plant / site code
Address and region
Warehouse and storage locations
Production or maintenance zones
Operational status (Active, Shutdown)
Manufacturing example
Plant: Houston #2
Plant Code: US-TX-H02
Function: Assembly & Testing
Warehouse: WH-A
Latitude: 29.7604° N
Operational Status: Active
Why it matters
Enables accurate inventory visibility by location
Supports inter-plant transfers and logistics planning
Improves traceability for audits and recalls
Helps maintenance teams locate assets and spares quickly
What it represents in manufacturing
Product Master Data defines what the company manufactures and sells, ensuring a single, consistent product definition across engineering, production, quality, sales, and compliance.
Typical attributes
Product code and standardized name
Technical specifications
Product family and classification
Lifecycle status (New, Active, Obsolete)
Regulatory and compliance information
Associated BOM and routing
Manufacturing example
Product: Stainless Steel Valve – 2 Inch
Product Code: PRD-2103
Pressure Rating: PN16
End Type: Flanged
Lifecycle Status: Active
Compliance: ASTM A351, PED certified
Why it matters
Ensures engineering, production, and sales use the same product definition
Prevents errors in BOMs and routings
Supports faster product launches and change management
Enables accurate costing, pricing, and regulatory compliance
What it represents in manufacturing
Service Master Data defines all the services an organization purchases, provides, or performs – from outsourced maintenance and calibration to inspection, consulting, or logistics services. It’s critical for managing contracted services, cost control, and vendor performance.
Typical attributes
- Service ID or code
- Standardized service description
- Service category (e.g., Maintenance, Calibration, Transport)
- Unit of Measure (Hour, Job, Lot)
- Associated supplier or contractor
- Service rate / pricing and currency
- Contract reference or SLA details
Manufacturing example
- Service ID: SRV-2041
- Description: Preventive Maintenance – Hydraulic Press
- Category: Maintenance Services
- Supplier: ABC Engineering Services
- Rate: $85/hour
- SLA: Next-business-day response
- UoM: Hour
Why it matters
- Ensures accurate and consistent service procurement and billing
- Avoids duplicate or ambiguous service entries in ERP
- Enhances vendor compliance to agreed SLAs and rates
- Improves visibility into outsourced service spend and performance
- Supports budgeting, cost allocation, and maintenance reliability tracking
The Master Data Lifecycle: What Actually Happens
Over time, this data becomes duplicated, incomplete, inconsistent, and outdated, leading to inefficiencies across procurement, maintenance, and production.
Without proper governance, manufacturers face recurring issues such as:
Inaccurate spare part identification and procurement delays.
Redundant inventory and inflated carrying costs.
Incorrect supplier or service information impacting operations.
Compliance and traceability challenges across plants and systems.
Implementing Master Data Management (MDM) addresses these challenges by establishing a single, standardized source of truth that ensures every system-from ERP to EAM-operates on clean, consistent, and connected data.
When MDM is implemented, here’s what actually happens:
Pull material, supplier, asset, inventory, product, and service master data from ERP, procurement systems, maintenance systems, inventory management systems, and legacy files. There may have 100,000+ records across multiple systems.
Find duplicates (e.g., “bearing-6205,” “cylindrical roller bearing,” “part #12345”).
Identify incomplete records (e.g., items without manufacturer or unit of measure).
Detect inconsistencies (e.g., units listed as “kg,” “Kgs,” “kilograms” instead of standardized “KG”).
Categorize every material, product, and service using standardized taxonomies (e.g., UNSPSC codes).
Example: “Stainless steel bolt” → UNSPSC 31161607.
This enables procurement to view total spending by category across suppliers and product/service lines.
Break down product, material, and service descriptions into searchable fields.
Example: “Centrifugal pump 20HP stainless impeller 440V 1450RPM” →
Type = Centrifugal Pump
Power = 20 HP
Material = Stainless Steel
Voltage = 440 V
Speed = 1450 RPM
This allows quick comparison across plants and service lines.
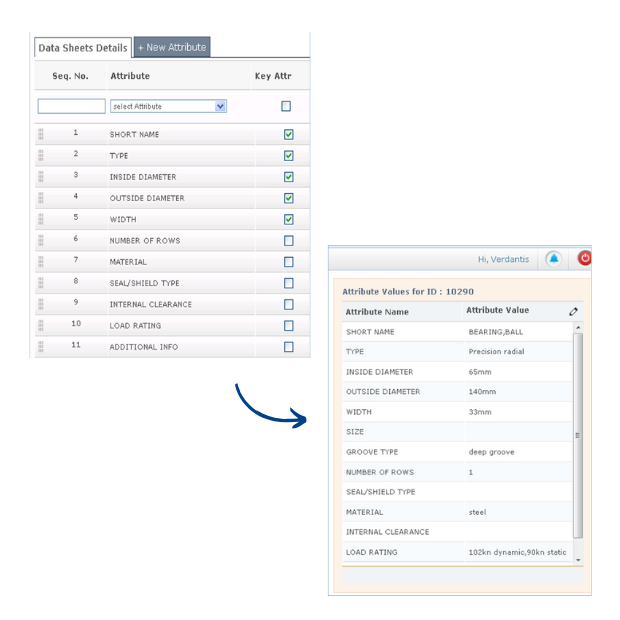
Add missing details from catalogs, manufacturer datasheets, or service specifications.
Example: Bearing now has bore = 25mm, outer diameter = 52mm, width = 15mm, precision = P6, supplier = SKF.
Services can be enriched with standard labor codes, SLA details, or service duration.
Recognize identical items despite naming differences:
“Motor 11kW 3PH ABB” and “ABB electric motor 11 kilowatt 3 phase” → merged.
Duplicate service entries (e.g., “Preventive Maintenance – Pump” vs. “Pump PM”) → merged.
Reduces redundancy in inventory, products, and services.
Evaluate each spare part based on:
Impact on asset uptime and safety
Failure consequences and lead time
Availability of substitutes or alternates
Cost vs. downtime risk
Assign criticality levels (Critical / Essential / Non-critical) to support:
Risk-based stocking strategies
Maintenance and shutdown planning
Prioritized procurement and expediting decisions
Flag obsolete, end-of-life, and slow-moving spare parts by analyzing usage history, OEM lifecycle status, and asset retirement plans.
Map replacement parts, alternates, or redesign options to prevent maintenance disruptions.
Clean, standardized data flows back into ERP, procurement, maintenance, inventory management, and quality systems.
Any update in product specifications or service instructions reflects across all systems.
Inventory sees accurate stock levels, maintenance sees correct asset info, procurement sees true supplier data.
Set mandatory rules: New materials, products, and services must have manufacturer/service code and unit of measure before approval.
Automated checks prevent duplicate supplier, product, or service codes.
Data stewards monitor data quality metrics weekly to ensure bad data doesn’t accumulate.
The Business Imperative
Organizations with robust MDM report up to 40% lower operational costs and 67% faster decision-making cycles, highlighting substantial efficiency gains and agility benefits.
Why the Value Chain Breaks
Manufacturing MDM is applicable across the entire manufacturing value chain, providing a single, trusted source of truth for critical data-products, materials, suppliers, customers, and assets. A unified data foundation enhances operational efficiency, quality control, supply chain visibility, and regulatory compliance throughout the lifecycle.
- Product Design and Engineering Lose Agility
Inconsistent product hierarchies and duplicate part entries slow down design cycles. Engineering teams waste time hunting for reusable components or approving redundant parts because the data doesn’t reveal their equivalence. Poor product master data leads to higher material costs from the start. - Procurement and Supplier Data Limit Strategic Leverage
When supplier information is fragmented across plants and ERP systems, sourcing loses its edge. Negotiations are based on partial spend data, and potential supplier consolidation opportunities go unseen. Procurement wastes hours verifying vendor codes and pricing data, while maverick purchasing grows unchecked. Harmonized supplier and procurement master data gives visibility into true spend, supplier performance, and risk exposure-turning buying power into strategic advantage. - Inventory and Materials Data Inflate Costs
There might be millions of dollars worth of parts across multiple sites that appear different but are identical. Inconsistent material descriptions cause search failures and duplicate purchases. Overstocking becomes a safety measure, not a strategy. Accurate materials data reduces inventory carrying costs, improves availability, and enables analytics-driven demand forecasting. - Production and Maintenance Struggle Without Trusted Data
Production planning depends on precise material, equipment, and BOM data. When these are out of sync, production runs stall, and maintenance teams can’t find the right spares quickly. Unscheduled downtime and low asset utilization follow. Harmonized asset and equipment data enable predictive maintenance, minimize downtime, and ensure operational continuity. - Quality and Compliance Are Jeopardized
Regulatory and quality data issues-like inconsistent component traceability or incomplete supplier certifications-turn audits into firefighting exercises. A single incorrect supplier record can obscure product lineage and compliance proof. Consistent master data ensures traceability, audit readiness, and confident quality assurance, protecting brand reputation. - Digital Transformation Falls Short Without Data Integrity
AI-driven analytics, IoT platforms, and digital twins all rely on high-quality master data. When the underlying records are inaccurate or incomplete, insights are distorted, and automation fails to scale. Digital transformation ROI diminishes because the data foundation cannot support advanced manufacturing initiatives.
For example: There’s $15 million worth of spare parts sitting across three warehouses. Maintenance searches fail because item descriptions are inconsistent, so teams reorder stock “just in case.” One bearing might appear as “6205 deep groove,” “ball bearing 25mm,” or “SKF part #12345”-all the same part, all clogging storage space.
For a company like this with $100-150 million in annual revenue, poor material master data alone inflates inventory costs by $1-1.4 million annually. That’s tied-up capital that could be driving growth instead of gathering dust in storage.
The Value Chain Is Only as Strong as Its Data
From design to sourcing, manufacturing to delivery, every function depends on consistent, connected information. Manufacturing MDM unifies data across domains-materials, products, suppliers, assets, and customers-creating a reliable foundation for decisions, innovation, and growth.
Clean data doesn’t just improve operations; it transforms the entire manufacturing value chain into a well-synchronized, data-driven enterprise.
Strategic and Technical Benefits: Efficiency, Quality, Compliance, and Cost Savings
Manufacturing organizations implementing comprehensive MDM manufacturing solution realize substantial strategic benefits across multiple functional areas.
MDM streamlines approval workflows and reduces manual checks, enabling faster decisio-making across departments.
Centralized and validated data accelerates material creation and reduces time spent searching for information.
Complete and deduplicated data prevents wrong part orders, reducing downtime and improving asset availability.
Enforcing structured data attributes ensures compliance and reduces ordering errors.
Governance processes improve data quality and completeness across the organization.
Standardized taxonomies and mandatory fields support industry regulations, audits, and traceability requirements.
MDM enhances efficiency in compliance processes and facilitates smoother cross-department collaboration.
Accurate and consistent master data reduces time spent correcting errors and searching for information.
High-quality master data forms the foundation for predictive maintenance, IoT, and smart manufacturing initiatives.
MDM supports faster readiness for digital transformation platforms like S/4HANA.
Consolidation of duplicate components and optimized inventory levels reduce operational and inventory carrying costs.
Rationalized vendors and materials across plants enable procurement savings.
Reliable and searchable supplier and product data reduces maverick spend and ensures better compliance with approved processes.
Value Drivers: Key Business and Operational Motivators
Value Driver | Impact on Operations |
Clean Material Data | Eliminates duplicates and enhances procurement efficiency |
Enriched Asset Data | Enables predictive maintenance and uptime reliability |
Unified Supplier Data | Strengthens sourcing and contract visibility |
Accurate BOMs | Reduces rework, improves production consistency |
AI-Powered Governance | Sustains long-term data quality |
Integrated Platforms | Aligns PLM, ERP, and MES data for full visibility |
Inventory Optimization and Working Capital
Duplicate detection and alternate part identification cut inventory by 10%, freeing millions in working capital. By eliminating duplicate and obsolete items, organizations significantly reduce excess MRO stock. AI-powered tools flag obsolete parts and identify inactive components.
Operational Uptime and Asset Reliability
Data-driven preventive maintenance and auto-enriched material masters ensure equipment downtime is minimized. An oil and gas leader implemented attribute-driven governance in master data, which averted high-cost stockouts and ensured correct “Radial” vs. “Standard” bearing selection, safeguarding production continuity.
Supplier Rationalization and Volume Discounts
Supplier rationalization through data-driven insights can reduce vendor count by 10-15% and unlock volume discounts. Aligning vendor and invoice data lowers mismatch rates by 30%, reducing delays in payment processing.
Enhanced Procurement Efficiency
Clean, classified service and material data improves supplier matching, bid creation, and quote comparisons. Trusted, enriched item/service master data guides users to preferred suppliers and contracts within procurement platforms. Time to onboard new vendors is dramatically reduced through automated validation and approval workflows.
Key Performance Indicators
Manufacturing organizations should track both leading and lagging indicators to measure master data management program effectiveness.
Based on our multi-year experience implementing Master Data Management programs across manufacturing clients, we have observed the following improvements:
Data Quality Metrics
- Completeness – Percentage of mandatory fields populated across master data domains
- Accuracy – Error rate in master data records validated against source systems or physical verification
- Consistency – Percentage of records conforming to naming conventions and standardization rules
- Timeliness – Average age of master data records and time to update after change events
Operational Impact Metrics
- Inventory carrying cost reduction – 10-15% target through duplicate elimination and rationalization
- Procurement cycle time improvement – Days to create purchase requisitions and complete sourcing
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) reduction – 15-20% improvement through enhanced asset and spare parts data
- Duplicate record elimination – Percentage reduction in duplicate materials, suppliers, and assets
- Data processing time reduction – 50%+ improvement in time required for data cleansing and enrichment
Business Value Metrics
- Working capital optimization – Millions freed through inventory reduction and improved cash conversion
- Procurement savings – 20-30% reductions through vendor rationalization and improved supplier management
- Production uptime improvement – Hours of downtime avoided through better spare parts availability
- Digital transformation acceleration – Months reduced from AI/ML implementation and ERP migration timelines
Quantifiable Impact Across Manufacturing Functions
Function | Key Metric | Improvement Achieved |
Maintenance & Reliability | Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) | ↓ 15-20% |
Inventory Management | Duplicate Items | ↓ 25-40% |
Procurement | Purchase Order Accuracy | ↑ 30% |
Operations | Data Processing Time | ↓ 50% |
Digital Transformation | S/4HANA Readiness | Accelerated by 40% |
These metrics demonstrate that MDM is not merely a data management initiative-it is a strategic program with quantifiable impact on core business metrics and operational performance.
Manufacturing MDM Success Stories
Food & Beverage Conglomerate: Mandatory Attribute Enforcement
A food and beverage client leveraged MDM to enforce mandatory “Food-Grade” attributes for pump parts. This governance rule eliminated ordering errors that could have led to contamination, product recalls, and regulatory penalties. The implementation improved first-time-right procurement, accelerated response times, and strengthened audit readiness.
Chemical Manufacturing Giant: Multi-Language Harmonization
A global chemical manufacturing company consolidated more than 100,000 unharmonized material master records across multiple languages into a single, unified source of truth. The project categorized, parsed, corrected, standardized, and enriched part data while eliminating duplicates and extracting insights from manufacturer names and part numbers.
Manufacturing Company: 100,000+ Records Enriched
A leading manufacturing company engaged AI enrichment to autonomously source missing data for material and service records. The implementation resulted in enriching over 100,000 material and service records within weeks, achieving over 30% cost savings in inventory management through enhanced data accuracy.
The Future of Manufacturing Data: AI-Driven MDM and Beyond
The manufacturing industry stands at an inflection point where AI-driven data quality is becoming the competitive differentiator between leaders and laggards in Industry 4.0 adoption.
AI-Driven Automation
Revolutionizing MDM by automating data cleansing, anomaly detection, and entity resolution. AI-native platforms reduce manual intervention by 40% while improving accuracy, enabling organizations to scale MDM across thousands of records efficiently.
Cloud-Native and Modular Architectures
Gaining widespread adoption. Over 80% of enterprises are expected to adopt cloud-native MDM platforms by 2026, driven by AI integration and hybrid architectures that support real-time collaboration and scalability.
Real-Time Processing and Unified Data Ecosystems
Represent the next frontier. MDM is shifting from static “golden records” to dynamic ecosystems that integrate streaming, transactional, and historical data, enabling real-time insights for predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization.
Multi-Domain and Cross-Industry Integration
Enables holistic analytics by consolidating customer, product, and supplier data. AI unifies siloed data to improve operational efficiency and compliance across departments.
Strengthened Governance and Compliance
Through automated frameworks that enforce policies in real time. AI-driven lineage tracking and predictive risk management ensure adherence to GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations.
The Path Forward: Self-Learning Data Ecosystems
The future lies in self-learning data ecosystems that continuously improve accuracy and context awareness, empowering enterprises to unlock the full potential of Industry 4.0 initiatives such as digital twins, predictive maintenance, and connected supply chains.
As manufacturing moves toward hyper-automation, the complexity of data continues to expand. Organizations that establish robust MDM foundations today will be positioned to implement advanced technologies effectively, while those without trusted master data will struggle with implementation delays and suboptimal outcomes.
Conclusion: Master Data as Strategic Asset
Master data is not just a record-it is a strategic asset. Clean, accurate, and harmonized master data drives efficiency, compliance, and innovation across the manufacturing enterprise.
From materials and inventory to assets and services, organizations that prioritize master data governance position themselves for:
- Reduced operational costs
- Enhanced production uptime
- Accelerated digital transformation
- Improved supply chain resilience
- Regulatory compliance
- Competitive advantage through faster decision-making
Manufacturing leaders who recognize MDM as foundational to business strategy will build organizations capable of thriving in an increasingly complex, data-driven, and automated industrial landscape. The path forward is clear: those who invest in manufacturing master data management today will operate with unprecedented operational clarity and agility tomorrow.
Verdantis stands as a trusted partner for global manufacturers-bringing together deep domain expertise, AI-powered automation, and decades of MDM experience to deliver trusted data at scale. Manufacturing executives who recognize MDM as foundational to business strategy will build organizations capable of thriving in an increasingly complex, data-driven, and automated industrial landscape.
What People Ask
What does Verdantis offer for Manufacturing Master Data Management?
Verdantis offers AI-powered master data management solutions purpose-built for manufacturing environments. The platform supports cleansing, standardization, classification, enrichment, and governance of material, spare parts, supplier, asset, and service master data across ERP, EAM, procurement, and legacy systems.
How does Manufacturing MDM support digital transformation initiatives?
Manufacturing MDM provides clean, standardized, and governed master data required for ERP modernization, S/4HANA migration, analytics, AI/ML initiatives, predictive maintenance, and smart manufacturing programs. It ensures digital initiatives are built on reliable data foundations.
What business outcomes can be expected from Manufacturing MDM?
Manufacturing MDM improves inventory visibility, reduces duplicate and obsolete materials, accelerates procurement and maintenance processes, improves asset uptime, supports compliance, and enables working capital optimization through better data-driven decision-making.
How often should manufacturing master data be cleansed and governed?
Master data cleansing should not be a one-time activity. Manufacturing MDM establishes continuous governance with workflows, validation rules, and ownership to ensure data quality is maintained as new materials, suppliers, and assets are created or modified.
How does Manufacturing MDM reduce inventory and carrying costs?
By identifying duplicates, standardizing material descriptions, and rationalizing similar or alternate parts, MDM improves inventory accuracy and visibility. This enables reduction of excess stock, lower safety stock levels, and improved inventory turnover.
Can Verdantis manage master data across multiple plants and ERPs?
Yes. Verdantis is designed to operate in complex, multi-plant, multi-ERP environments, synchronizing master data across systems such as SAP, Oracle, Maximo, Ariba, Coupa, and other manufacturing applications.
How does Manufacturing MDM support maintenance and reliability teams?
MDM ensures accurate spare parts, asset hierarchies, and attribute-rich material data, improving part identification, reducing repair delays, and supporting better maintenance planning and execution.
Is Manufacturing MDM relevant only for large enterprises?
Manufacturing MDM delivers value for both large and mid-sized manufacturers, especially those undergoing ERP upgrades, plant expansions, mergers, or inventory optimization initiatives.





