En las organizaciones actuales, impulsadas por los datos, la gestión de la información ya no es opcional, sino fundamental para la supervivencia. Pero no todos los datos son iguales.
Algunos datos impulsan a toda la empresa, mientras que otros impulsan lo que sus clientes ven realmente. Aquí es donde Gestión de datos maestros (MDM) y la gestión de la información sobre productos (PIM).
Piénselo de este modo: MDM es el cerebro de la empresa, que mantiene toda la información crítica precisa, coherente y fiable.
PIM es la voz de la empresa, que garantiza que el contenido de sus productos sea claro, esté enriquecido y listo para atraer a los clientes allí donde compren.
¿Qué problemas resuelven MDM y PIM?
MDM: la columna vertebral
MDM resuelve un problema muy específico: cómo crear una única fuente de verdad en toda una organización.
Sin MDM, las organizaciones suelen tener dificultades:
Materiales, datos de clientes o productos duplicados o contradictorios.
Informes y análisis imprecisos
Riesgos de conformidad y reglamentación
Ineficacia operativa debida a la falta de coherencia de los datos entre departamentos.
Por ejemplo, imagine una empresa de fabricación global que realiza el seguimiento de proveedores, almacenes y clientes a través de múltiples ERP.
Sin MDM, un mismo proveedor podría aparecer tres veces con nombres ligeramente distintos, lo que daría lugar a pagos duplicados, retrasos en los envíos o asignaciones de material erróneas.
MDM centraliza todos los datos críticos, los valida, los limpia y los distribuye a los sistemas posteriores para que todos, desde finanzas hasta operaciones, hablen el mismo idioma.
PIM - En primera línea
Mientras que MDM gobierna la empresa, PIM gobierna el contenido del producto para ventas y marketing.
Sin PIM:
Los catálogos de productos pueden ser incoherentes en el comercio electrónico, los mercados y las tiendas.
Las imágenes que faltan, las descripciones erróneas o los precios incorrectos frustran a los clientes.
Los equipos de marketing pasan horas copiando manualmente contenidos en múltiples plataformas
PIM centraliza toda la información relacionada con los productos, atributos, imágenes, descripciones, vídeos y certificaciones, y garantiza la preparación del canal.
Es el sistema que garantiza que tu página de Amazon, tu tienda de Shopify y tu punto de venta digan lo mismo sobre tus productos.
Diferencias clave: MDM frente a PIM
| Característica | Gestión de datos maestros (MDM) | Gestión de la información sobre productos (PIM) |
|---|---|---|
| Propósito | Coherencia de datos, conformidad y registros de oro en toda la empresa | Contenidos de productos precisos, enriquecidos y listos para el cliente |
| Alcance | Multidominio: Producto, Proveedor, Cliente, Servicio, MaterialesUbicación, Finanzas | Centrado en el producto: SKU, atributos, soportes, descripciones |
| Usuarios principales | TI, Administradores de datos, Analistas de datos, Científicos de datos | Marketing, Comercio electrónico, Gestores de contenidos de productos |
| Enfoque | Precisión, visión de 360°, eficacia operativa | Velocidad de comercialización, conversión, coherencia de canales |
| Disparadores | Duplicación de datos, mandatos normativos, incoherencias operativas | Ampliación del catálogo, nuevos canales de venta, actualización de productos |
| Integración | ERP, CRM, BI, Analítica | Plataformas de comercio electrónico, CMS, Marketplaces, DAM |
| Objetivo | Gobernanza y cumplimiento orientados a la empresa | Enfoque estratégico de las ventas/comercialización de productos |
| Equipos Propietarios | Equipo técnico de TI, administradores de datos operativos, expertos de dominio | Marketing, gestores de contenidos de productos, equipos de comercio electrónico |
¿Cómo funcionan?
MDM
PIM
Imagine que una empresa desea tener una visión de 360° de sus proveedores.
Paso 1: Crear
- Los datos brutos de los proveedores proceden de múltiples ERP, sistemas de aprovisionamiento y hojas de cálculo.
- Las entradas duplicadas se marcan y se limpian.
Enriquecimiento automático de datos mejora estos datos extrayendo información relevante de fuentes externas de confianza, como calificaciones de proveedores, métricas de salud financiera o datos de cumplimiento normativo.
Paso 2: Combinar y combinar
El sistema identifica que "Acme Ltd.", "Acme Ltd Inc." y "ACME Corporation" son la misma entidad.
Se crea un único registro de oro.
Depuración y normalización de datos maestros en MDM garantiza que los sistemas posteriores consuman un único registro de oro en lugar de entidades fragmentadas y duplicadas.
Paso 3: Aprobar
- Los Data Stewards revisan y validan el registro.
Paso 4: Distribuir
- Este registro verificado del proveedor se envía a los sistemas de compras, finanzas, logística y análisis.
Por qué es importante: Cuando se emite la siguiente orden de compra, el sistema garantiza que se paga al proveedor correcto, que la factura coincide y que los informes son precisos en todos los departamentos.
Sigamos un producto desde el concepto hasta el punto de contacto con el cliente:
Paso 1: Importar y enriquecer
- Los datos de los productos (SKU, especificaciones, imágenes) se importan del ERP o de los catálogos de los proveedores.
- Marketing añade descripciones enriquecidas, vídeos y localización.
Paso 2: Validación y preparación del canal
- Las normas de integridad garantizan que no falten atributos obligatorios en ningún producto.
- El formato específico para cada canal garantiza que el mismo producto tenga un aspecto perfecto en Amazon, Shopify y el sitio web de la empresa.
Paso 3: Sindicación
- Los datos se envían a múltiples canales de venta en tiempo real.
- Los clientes ven contenidos precisos y enriquecidos que reducen las devoluciones y aumentan las conversiones.
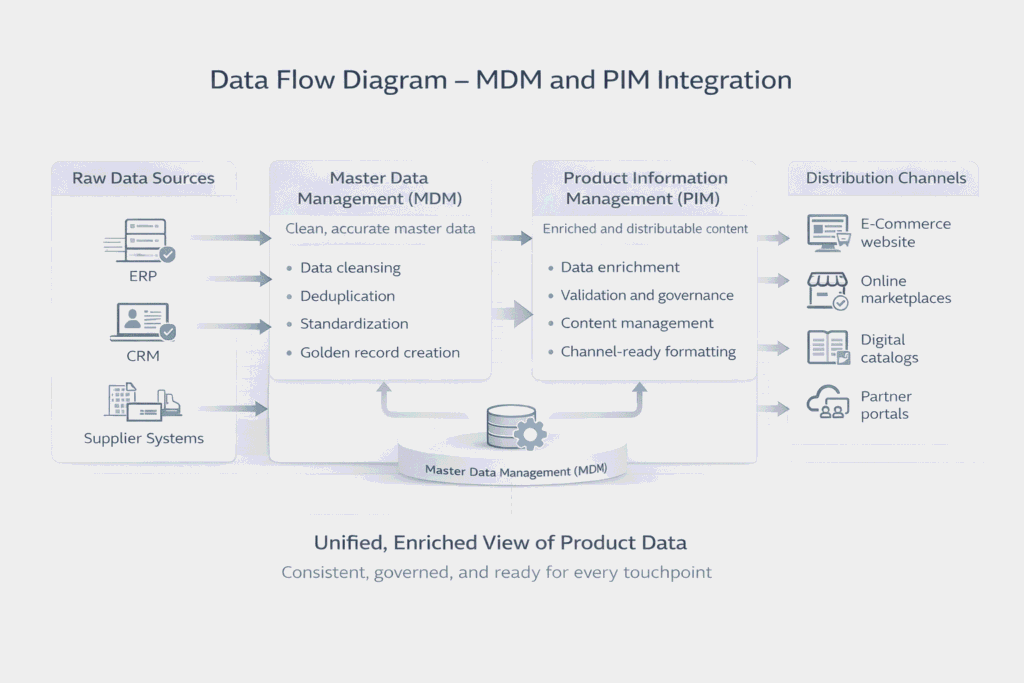
MDM + PIM en tándem: un escenario del mundo real
Imagina un empresa mundial de electrónica lanzando un nuevo termostato inteligente:
MDM limpia los datos:
- Garantiza que el producto, los proveedores y las plantas de fabricación se registran con precisión.
- Verifica la conformidad, los códigos fiscales y las correspondencias financieras.
El PIM enriquece el contenido del producto:
- Añade imágenes, manuales, funciones y descripciones multilingües.
- Prepara contenidos para Amazon, tiendas físicas y sitios web regionales.
Resultado:
- Los sistemas internos disponen de datos operativos precisos.
- Los clientes ven contenidos de productos coherentes y atractivos en todos los canales.
Equipos propietarios y gestores de MDM y PIM
Propiedad de MDM
- Equipo técnico de TI: Implanta y mantiene las herramientas y la infraestructura de MDM para construir los sistemas propietarios de los datos maestros, gestionando aspectos tecnológicos como la seguridad y la integración.
- Expertos en dominios: Tienen la máxima autoridad y responsabilidad sobre dominios de datos específicos para definir la finalidad de los datos, la visión estratégica y adoptar políticas dentro de su dominio.
- Responsables de datos operativos: Personas centradas en el negocio que gestionan datos y resuelven problemas para satisfacer las necesidades empresariales. Actúan como puente clave entre la empresa y el departamento de TI para garantizar la fiabilidad de los datos.
Propiedad de PIM
- Equipos de marketing: Son usuarios primarios que utilizan PIM para crear experiencias de compra de productos, gestionar activos digitales y estructurar el contenido de campañas variadas.
- Equipos de comercio electrónico: Estos equipos confían sobre todo en PIM para garantizar datos actualizados y precisos de los productos en todos los sitios web de comercio electrónico y zonas de mercado para impulsar el ratio de ventas y reducir las tasas de devolución.
- Gestores de contenidos de productos: Estos especialistas gestionan los datos rutinarios, la localización y las aprobaciones de calidad dentro del sistema PIM.
- Equipos de ventas: Utilizan PIM para acceder rápidamente a información precisa sobre productos y materiales para las interacciones con los clientes y la asistencia en ventas.
Casos de uso de PIM y MDM en diferentes sectores
| Industria | Casos de uso de MDM | Casos de uso de PIM |
|---|---|---|
| Venta al por menor y comercio electrónico | Vista única de productos/clientes en todas las tiendas y ERP | Gestión de catálogos de productos, sindicación de canales |
| Fabricación | Gestión de datos de proveedores y materiales | Especificaciones de productos y contenidos de marketing |
| Sanidad | Cumplimiento de los datos de pacientes y proveedores | Instrucciones del producto, contenido normativo |
| Finanzas | Cliente 360°, informes de cumplimiento | N/A |
| Distribución y venta al por mayor | Datos sobre proveedores/clientes/productos para la cadena de suministro | Catálogos de productos multicanal |
Ingeniería del ciclo de vida de los datos MDM y PIM
MDM y PIM funcionan en paralelo, pero sus flujos de trabajo técnicos difieren:
| Etapa del ciclo de vida | Acción MDM | Acción PIM | Notas técnicas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingesta de datos | Extrae datos de ERP, CRM y sistemas heredados | Extrae la información básica del producto de MDM | Canalizaciones ETL/ELT, conectores API |
| Limpieza y validación | Deduplicación, normalización, reglas de validación | Comprobaciones de integridad, validación de atributos | Motor de reglas, detección de anomalías ML |
| Enriquecimiento | Añada clasificaciones, información sobre proveedores y precios | Añadir descripciones, imágenes y metadatos SEO | AI/NLP para la copia, integración DAM para los medios de comunicación |
| Aprobación y gobernanza | Aprobaciones de flujos de trabajo, gestión de excepciones, normas de supervivencia | Aprobaciones de lanzamiento de canales, aprobaciones de localización | Control de acceso basado en funciones, flujos de trabajo BPM |
| Sindicación | Publicar el registro de oro en ERP, BI, análisis | Exportar a comercio electrónico, mercados, CMS | Alimentación API, transformación de formatos (JSON, XML, CSV) |
| Comentarios y análisis | Cuadros de mando de la calidad de los datos, excepciones, conciliación | Conversión, catálogo completo, métricas de campaña | Cuadros de mando de BI, conocimientos de ML, circuitos de retroalimentación |
Escenario: Lanzamiento de 50.000 nuevas referencias para la temporada de invierno
| Escenario | Acontecimiento real | Acción MDM | Acción PIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creación SKU | El proveedor presenta el catálogo | MDM deduplica, valida la SKU maestra, asigna un identificador global | SKU base introducida en el PIM |
| Enriquecimiento | Marketing crea campañas | MDM garantiza la coherencia de precios y categorías | PIM añade imágenes, vídeos, descripciones y metadatos SEO |
| Sindicación de canales | Publicar en Amazon, Shopify, sitio web | ERP recibe el SKU de oro | PIM transforma los datos a formatos específicos del canal |
| Comentarios | Recopilación de datos sobre conversiones y clics | MDM concilia las actualizaciones de proveedores y ERP | El PIM señala los contenidos que faltan o las referencias de bajo rendimiento |
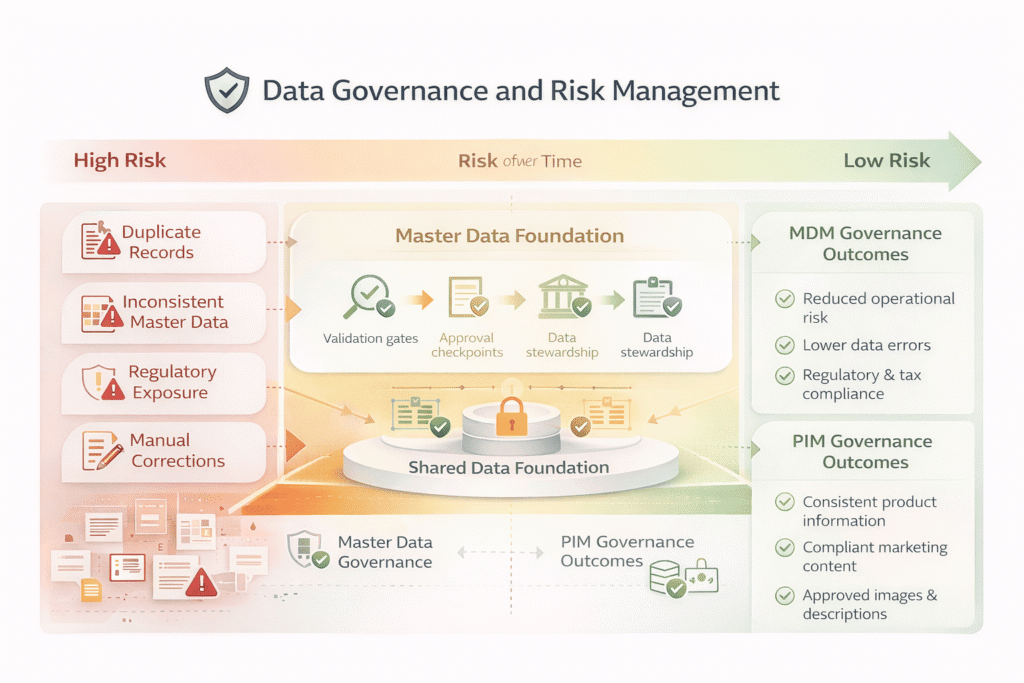
¿Cuándo implantar MDM y PIM a la vez?
1. Demandas urgentes de comercio electrónico y problemas de datos sistémicos adversos: Un enfoque paralelo permite obtener resultados más rápidos con PIM en los canales orientados al cliente, mientras que MDM se centra en las incoherencias de los datos fundacionales de la planta.
2. Sectores como el manufacturero, el minorista, el farmacéutico o el financiero suelen requerir MDM para una gobernanza y un cumplimiento estrictos en todos los dominios de datos (cliente, producto, proveedor, etc.), mientras que PIM se utiliza para gestionar las especificaciones de productos de cara al público y el contenido de marketing.
3. MDM puede gobernar los datos internos de la cadena de suministro y ofrecer un viaje seguro completo, mientras que PIM garantiza que el contenido del producto es preciso y está enriquecido.
Este flujo de datos optimizado y enlazado proporciona una imagen completa para tomar decisiones acertadas y obtener resultados finales más rápidos.
4. Perseguir una transformación digital global compleja o escalar: El rápido crecimiento crea complejidades de datos en múltiples frentes.
El uso de sistemas PIM y MDM proporciona la base necesaria para iniciativas mejoradas como las recomendaciones basadas en IA en mercados globales y múltiples canales de venta.
5. Aprovechar la IA tanto para la experiencia del cliente como para la eficiencia interna: MDM proporciona la base de datos fiables, precisos y limpios necesaria para entrenar modelos de IA para análisis internos, mientras que PIM utiliza la IA para el enriquecimiento automatizado de contenidos, el etiquetado inteligente y la localización para mejorar la experiencia del cliente.
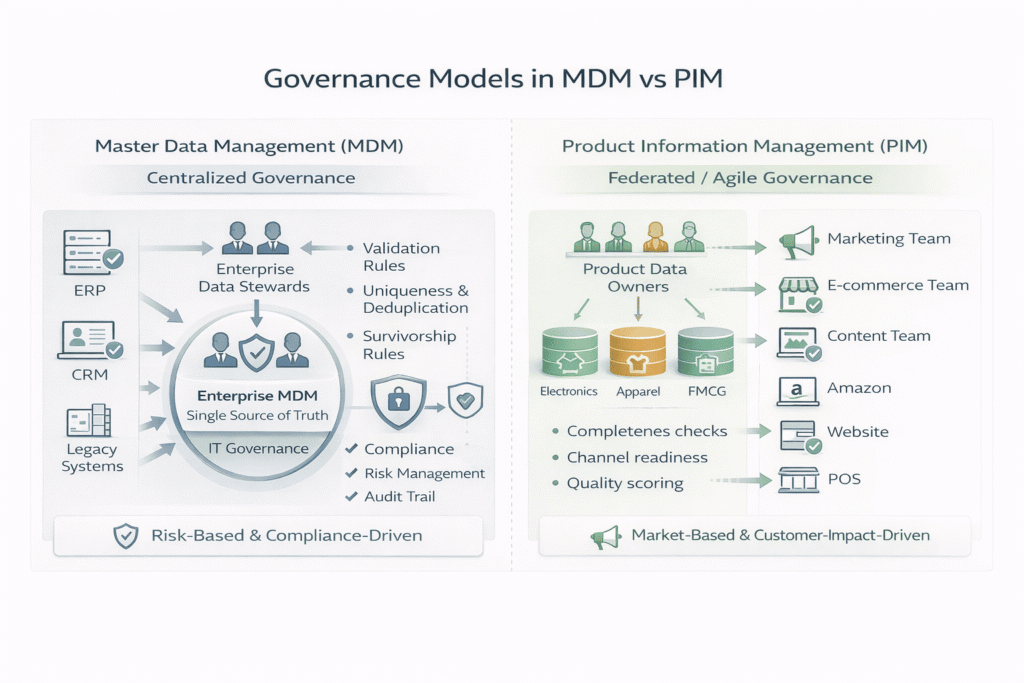
Modelos de gobernanza: Centralizado vs Federado
Límites de la custodia de datos
- Administradores de datos empresariales (MDM): Los administradores de datos empresariales en MDM son los expertos empresariales cruciales que gobiernan y gestionan toda la calidad de los datos maestros de una organización (como información sobre productos, clientes o activos) resolviendo problemas, tendiendo puentes entre la empresa y TI y aplicando políticas para crear datos fiables.
- Propietarios de datos de dominio o producto (PIM): Un propietario de datos de producto es una persona o equipo responsable de la integridad, precisión, gobernanza y enriquecimiento de una categoría o dominio específico de datos de producto dentro de la organización.
¿Por qué difieren las vías de escalada de la gobernanza?
La MDM implica una gobernanza empresarial dirigida por TI con escalado interfuncional, mientras que la PIM se centra en el enriquecimiento de datos relacionados con productos y dirigidos a marketing/negocio con flujos de trabajo más ágiles.
Aplicación de políticas frente a control editorial
MDM impone:
1. Reglas de validación: Se trata de un conjunto de reglas de datos que comprueban su integridad a medida que se procesan. Las reglas de validación aplican formatos estándar que garantizan que los campos críticos no queden en blanco, o verifican los datos con fuentes externas, para evitar datos basura.
2. Singularidad: MDM garantiza que cada elemento tenga un identificador único y evita los registros duplicados en el sistema. Esto incluye el uso de técnicas como la concordancia difusa para encontrar registros que identifiquen la entidad similar, aunque los datos contengan ligeros errores.
3. Supervivencia: Cuando el sistema MDM identifica datos duplicados de diferentes fuentes para el mismo artículo, las reglas determinarán qué valores de datos deben conservarse para rellenar el registro maestro.
PIM impone:
1. Integridad: Los sistemas PIM utilizan sólidas reglas de validación para garantizar que todos los atributos obligatorios están presentes antes de que un producto pueda lanzarse al mercado. Así se evita que lleguen a los puntos de contacto con el cliente productos a los que les falta alguna formación (por ejemplo, una especificación clave).
2. Preparación del canal: PIM ayuda a las empresas a formatear la información de los productos para adaptarla a los requisitos específicos de los distintos canales (por ejemplo, mercados como Amazon o sitios web de comercio electrónico).
3. Puntuación de la calidad: Las soluciones PIM avanzadas generan informes completos que ponen de manifiesto las incoherencias de los datos. Estas medidas ayudan a solucionar antes los problemas de datos, garantizando la coherencia de la información.
Flujos de aprobación: Basados en el riesgo frente a los basados en el mercado
Homologaciones MDM impulsada por el cumplimiento y el riesgo descendente:
- MDM supera los conflictos entre diferentes plantas y departamentos. Esta gestión proactiva de los datos se erige en única fuente de verdad para explicar el cumplimiento coherente de la normativa en toda la organización. MDM simplifica y respalda el cumplimiento de la normativa e impulsa la eficiencia.
- La coherencia de los datos evita problemas como el retraso en las promociones de productos o las controversias en la cadena de suministro, que contribuyen a la mala calidad de los datos.
Homologaciones PIM se rigen por la coherencia de la marca y el impacto en el cliente:
Coherencia de marca:
- Sólo los activos digitales centralizados con PIM garantizarán que los logotipos y las imágenes de marca se utilicen en todos los puntos de contacto.
- Mantener directrices específicas para cada canal con PIM permite adaptar contenidos precisos y coherentes a audiencias específicas de plataformas variadas.
- El PIM insiste en la estandarización de las descripciones y los mensajes, evitando así que la promoción de la marca se diluya entre los miembros del equipo y los canales.
Impacto en el cliente
- Los datos enriquecidos de los productos permiten una experiencia de compra personalizada que reduce los problemas e incertidumbres posteriores a la compra.
- Las aprobaciones PIM garantizan que los clientes reciban información fiable y completa sobre los productos, ya que los datos incompletos provocan quejas de los clientes y reducen su satisfacción.
- Las experiencias coherentes en todos los canales de la tienda generan confianza en la fiabilidad de la marca.
IA y automatización en MDM/PIM
Las plataformas MDM/PIM modernas integran cada vez más IA y automatización:
MDM: Alertas predictivas sobre la calidad de los datos, detección de anomalías, deduplicación automatizada, sugerencias de clasificación.
PIM: Enriquecimiento automatizado de contenidos (PNL para descripciones), etiquetado inteligente de imágenes, localización mediante ML.
Impacto integrado: Reduce las intervenciones manuales, acelera el lanzamiento de SKU, garantiza el cumplimiento y mejora los análisis.
Impacto empresarial y KPI
| Métrica | Impacto de MDM | Impacto del PIM |
|---|---|---|
| Eficiencia operativa | 15-25% reducción de los costes operativos (Fuente) | Gestión de datos de productos 6 veces más rápida (Fuente) |
| Reducción de errores | 40-60% menos duplicados/errores | 20-50% mayor conversión gracias a un contenido preciso |
| Inventario y cadena de suministro | 10-20% reducción de las incoherencias de existencias | La sindicación de SKU reduce las roturas de stock |
| Tiempo de comercialización | Ciclos de lanzamiento de productos más rápidos (2×) | Enriquecimiento y sindicación más rápidos a los canales |
| Conformidad | 50-70% menos cuestiones reglamentarias relacionadas con los datos | Garantiza el cumplimiento de las normas legales y de marketing en el contenido de los productos. |
MDM y PIM, aunque distintos en su enfoque, trabajan juntos para proporcionar una base de datos sólida para las organizaciones modernas.
MDM garantiza que los datos empresariales básicos sean precisos, coherentes y fiables en toda la empresa, mientras que PIM ofrece información de producto enriquecida y preparada para el cliente que impulsa un mayor compromiso y conversiones.
La combinación de estos sistemas, mejorada por funciones como el enriquecimiento automatizado y la limpieza de datos maestros, permite a las empresas agilizar las operaciones, mejorar la experiencia del cliente y adelantarse a las demandas del mercado.
Al alinear ambos, las organizaciones no solo pueden mantener la integridad de los datos, sino también maximizar su eficiencia y adaptabilidad en un mundo digital en rápida evolución.





