In Master Data Management, a Service Master Data Record is the reference data and information that captures the nature of a service, along with details like the service category, Unit of Measure for the Service and a few other static details.
Every single record in a Service Master represents a “unique service” and only one record should exist for representing that specific service, in almost all ERPs this record is tagged with an ID, commonly known as a service ID.
In any ERP system, a Service Master Data Record is the golden record that standardizes every service a company procures. It contains critical data fields: a unique service identifier, standardized descriptions, unit of measure (UOM), category classification, and service specifications. Each record represents exactly one unique service, enabling consistent procurement, accurate billing, and reliable vendor management across the enterprise.
The MDM market itself is experiencing explosive growth-valued at USD 18.23 billion in 2025, with projections to reach USD 43.38 billion by 2030 (CAGR of 18.93%), driven largely by organizations recognizing the strategic value of master data governance.
Src: Mordor Intelligence
Here’s an example of what a Service Master Data record looks like. The service is “simplified” in this case.
Service ID | Service Name | UOM | Category | UNSPSC Code | Specification |
SVC-0150 | Hydraulic Pump Preventive Maintenance | HOUR | Mechanical Maintenance | 73152101 | ISO-certified vendor, quarterly inspections |
SVC-0275 | Pressure Vessel Annual Inspection | EA | Compliance/Safety | 81101614 | Third-party certified inspector required |
SVC-0420 | Calibration Service – Temperature Sensor | EA | Instrumentation | 73161503 | NIST-traceable, certification provided |
SVC-0530 | Electrical System Commissioning | DAY | Engineering Services | 73140200 | L3 certification, factory acceptance testing |
Service Master Data Model
A Service Master in SAP MM, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics follows a consistent data architecture:
Column Name | Description | Example Data | Importance |
Service Number | The unique, non-changing ID used to reference the service throughout the system. | SVC-0010 | Primary Key – Essential for linking and searching. |
Service Short Text | A standardized, concise description. Must be unique. | Pump Repair Service (Model X) | Used on Purchase Orders and invoices. |
Service Long Text | A detailed scope of work or general specification. | See attached SOW V2.0. Requires L3 Tech. | Provides clarity on deliverables. |
Base Unit of Measure (UoM) | The unit in which the service is measured and procured. | HOUR, DAY, EA (Each), MTR (Meter) | Required for quantity tracking and pricing. |
Service Specifications | Specific requirements that should be met while availing this service | For example; must be a service from an ISO-compliant vendor, or a CMRP certified maintenance professional | For ensuring standards and protocols are met |
In some cases, the service master also references to a sub-table that itemizes and details the specifics of the service – this is particularly true for frequently recurring services like a planned preventive maintenance check.






Types of Services Captured in a Service Master
All non-physical engagements that don’t include software subscriptions and material or Capex purchases are captured in a Service Master.
Who Uses Service Master Data?
1. MRO, Maintenance & Production Teams
These include services availed for maintenance contracting, Reliability Engineering, setting up Predictive Maintenance systems, Preventive inspection and upkeep of facilities and equipment.
For predominantly production-oriented enterprises, MRO, Maintenance & Manufacturing services form a bulk of the service master data records.
Also, for a multi-domain, unified MRO master data view, these service master records need to be integrated with other data domains relevant to maintenance and supply chain teams.
This primarily includes material master, supplier master and fixed asset master data. This is also why the Service Master Data sits in the MM (Material Management) module, at least in SAP.
Types of services captured
- Preventive maintenance services
- Breakdown and corrective maintenance contracts
- Reliability engineering services
- Condition monitoring and predictive maintenance services
- Equipment calibration and inspection
- Facility maintenance services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-1001 | Pump Overhaul Service | EA | Mechanical Maintenance |
SVC-1002 | Vibration Analysis Service | HOUR | Reliability Engineering |
SVC-1003 | Annual Pressure Vessel Inspection | EA | Statutory Inspection |
SVC-1004 | Electrical Panel Preventive Maintenance | DAY | Electrical Maintenance |
These service records are typically used by:
- Maintenance planners
- Reliability engineers
- Asset managers
- Plant maintenance teams
Multi-domain integration requirement
For MRO-driven organizations, Service Master Data cannot function in isolation. It must be integrated with:
- Material Master Data
(spare parts and consumables required during service execution) - Fixed Asset / Equipment Master Data
(to link services to specific machines or production assets) - Supplier Master Data
(external maintenance contractors, inspection agencies, OEM service providers)
This tight integration enables:
- Accurate maintenance costing per asset
- Traceability of services performed
- Improved MRO inventory planning
- Better lifecycle cost analysis
This is also the primary reason why, in SAP, Service Master Data resides within the MM (Materials Management) module, which governs procurement for both materials and services.
2. Finance & Accounts Payable Teams
These teams Primarily make use of the systems to ascertain the nature of the services and for processing the invoices and undertaking spend analytics.
These teams may also make the entries themselves if they contract external teams for support with finance and accounting
Finance and AP teams rely on Service Master Data primarily for invoice processing, cost classification, and spend analytics.
While they may not always create service records, they are major consumers of service master data.
Types of services captured
- Accounting and bookkeeping services
- Audit and taxation services
- Financial advisory and consulting
- Payroll processing services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-3001 | Statutory Audit Services | EA | Audit |
SVC-3002 | Tax Advisory Services | HOUR | Financial Consulting |
SVC-3003 | Payroll Processing Services | MONTH | Finance Operations |
Finance teams use these records to:
- Match invoices accurately
- Classify spend by nature of service
- Analyze vendor-wise and category-wise costs
- Ensure correct GL postings
In some organizations, finance teams may also create service records when engaging external accounting or compliance agencies.
3. IT & Software Development Teams
This includes software services with specialist development agencies, implementation partners and offshore teams for building and deploying software applications.
IT organizations rely heavily on external service providers, making service master data critical for digital operations.
Types of services captured
Software development services
ERP and application implementation services
System integration and migration services
Cloud infrastructure support
Managed IT services
Cybersecurity and audit services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-2001 | SAP S/4HANA Implementation Consulting | HOUR | IT Consulting |
SVC-2002 | Application Development – Java | HOUR | Software Development |
SVC-2003 | Cloud Infrastructure Support | MONTH | Managed Services |
SVC-2004 | Cybersecurity Assessment Service | EA | IT Security |
These records are used by:
IT procurement teams
Digital transformation offices
PMOs
Finance for capitalization vs expense tracking
Standardized service masters help IT teams avoid duplicate consulting entries and enable better visibility into IT spend by service category.
4. Marketing & Communications
Services spanning marketing content, video production, creative writing, performance marketing and PR are also entered in the service master data.
Marketing functions increasingly depend on external agencies and creative partners, making service master governance essential.
Types of services captured
- Creative content development
- Video and media production
- Digital marketing services
- Performance marketing campaigns
- Public relations and branding services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-4001 | Corporate Video Production | EA | Media Services |
SVC-4002 | Social Media Campaign Management | MONTH | Digital Marketing |
SVC-4003 | PR & Media Outreach Services | MONTH | Public Relations |
SVC-4004 | Website Content Development | HOUR | Creative Services |
These standardized records help organizations:
- Track marketing spend accurately
- Compare agency performance
- Avoid duplicate service codes across regions
- Improve budgeting and ROI measurement
5. Supply Chain & Logistics Teams
Services specific to warehousing, breaking bulk, material handling and transportation (logistics) and created in the “Services Master”.
This also includes services pertaining to production supply chains like storeroom management, stock keeping, sorting etc.
While there are separate modules that track the details to of these services, one record for the specific service is created in the “Service Master”
Due to the complexity of these services, their specific details like Route, Carrier, Freight prices etc. are captured in separate modules, like the “transportation master” in SAP “Transportation Management”
Supply chain organizations consume a wide range of logistics and operational services, all of which are maintained in the Service Master.
Types of services captured
- Transportation and freight services
- Warehousing services
- Material handling and loading/unloading
- Storeroom management services
- Packaging and labeling services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-5001 | Road Transportation – Full Truck Load | TRIP | Logistics |
SVC-5002 | Warehouse Handling Services | TON | Warehousing |
SVC-5003 | Storeroom Management Services | MONTH | Inventory Operations |
SVC-5004 | Container Unloading Services | EA | Material Handling |
While detailed logistics parameters such as:
- Route
- Carrier
- Freight rates
- Delivery zones
are maintained in specialized modules (e.g., SAP Transportation Management), one standardized service record still exists in the Service Master to represent the service itself.
This ensures consistent procurement and financial tracking across the supply chain.
A multi-domain master data approach – integrating service, supplier, material, and logistics data – significantly improves supply chain visibility and control.
This article captures all the supply chain master data domains, and how a multi-domain approach to master data can empower supply chain teams.
6. Legal & Compliance Teams
Legal, auditory and consulting services along with a brief description of their nature are also captured with reference to the law firm/independent solicitor in charge of fulfilling that service.
Legal and compliance functions also depend on external professional services.
Types of services captured
- Legal advisory services
- Litigation support
- Compliance audits
- Regulatory consulting
- Intellectual property services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-6001 | Corporate Legal Advisory Services | HOUR | Legal Services |
SVC-6002 | Regulatory Compliance Audit | EA | Compliance |
SVC-6003 | Contract Review & Vetting | EA | Legal Review |
These records are linked to:
- Law firms
- Independent consultants
- Regulatory agencies
They help organizations track legal spend, manage engagements, and maintain audit readiness.
Where is the Service Master Configured in an ERP?
The configuration, structure, and storage of Service Master Data varies significantly across ERP platforms.
This variation exists because ERP systems were historically designed around procurement and financial control, not around the physical or non-physical nature of what is being procured. As a result, each ERP treats services differently depending on how its procurement architecture was designed.
Broadly, ERP systems follow one of two approaches:
Dedicated Service Master object (example: SAP, Infor LN)
Service treated as a non-stock item within Item Master (example: Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics)
Understanding where the Service Master resides is critical for data governance, integrations, and enterprise-wide reporting.
Service Master in SAP
In SAP, the “Service Master” table exists within the MM (Materials Management Module).
While it may seem counterintuitive since Services span several different functions, it is important to understand that SAP MM is primarily responsible for “procurement” processes.
This not only includes tangibles like materials, but also procurement of services.
Since a “Service Master” is quite relevant as a Master Data Domain for Procurement Processes, it resides within the MM module but is used across the Org.
Even companies in non-manufacturing and non-production operations make use of the “Materials Management” module since it’s a generic module responsible for procurement and supply chain management for enterprise operations.
Master data domains in SAP, how they are configured and their capabilities are covered in this article
Read More
In SAP, the Service Master exists within the MM (Materials Management) module.
At first glance, this may appear counterintuitive-since services are intangible and span departments such as IT, Finance, Legal, and Maintenance. However, the placement of Service Master Data within MM is intentional and architecturally sound.
Why SAP places Service Master in MM
SAP MM is fundamentally responsible for procurement processes, not just materials.
Procurement in SAP includes:
- Purchase of physical materials
- Procurement of external services
- Vendor management
- Contract management
- Invoice verification
Since services are procured from external vendors, they logically fall under the same procurement lifecycle as materials.
Therefore, the Service Master is modeled as a procurement master data object, even though it is consumed by multiple business functions.
How Service Master works in SAP
In SAP, a Service Master record typically contains:
Field | Example |
Service Number | SVC-100012 |
Short Text | Pump Overhaul Service |
Long Text | Complete dismantling, inspection and reassembly of centrifugal pump |
Unit of Measure | HOUR / EA |
Service Category | Mechanical Maintenance |
Classification | UNSPSC / Internal taxonomy |
These service records are used in:
- Service Purchase Requisitions
- Service Purchase Orders
- Service Entry Sheets (SES)
- Invoice Verification
Example SAP usage flow
- Maintenance team raises a work order requiring external pump repair
- Buyer creates a Service PO using Service Master: “Pump Overhaul Service”
- Vendor performs the work
- Maintenance confirms completion via Service Entry Sheet
- Finance posts invoice against the same service code
The same Service Master record is therefore used by:
- Maintenance
- Procurement
- Finance
- Asset accounting
Why SAP MM is used even by non-manufacturing companies
Even organizations that do not manufacture products-such as IT services firms, banks, or utilities-still use SAP MM because it functions as a generic enterprise procurement module.
Whether an organization is procuring:
- Consulting services
- Legal advisory
- Software development
- Facility management
…the procurement process remains the same, which is why Service Master Data resides centrally in MM and is shared across the organization.
Service Master in Oracle
In Oracle systems, a Service Master does not reside as a different object, instead, it resides within the same master data that manages materials. In Oracle systems, this is referred to as “Item Master Data” that captures data pertaining to tangible materials as well as “Services”
To effectively distinguish a Service data record from a Materials, Oracle users refer to specific attributes and their values set at an Item level.
This includes;
- Stockable (Attribute) – Set to NO
- Inventory Asset Value – Set to NO
- Purchasing Tab – Relevant Purchasing Attributes (UOM, Price, etc) are defined here, similar to standard material
Read More
Oracle ERP systems follow a different architectural approach.
In Oracle, there is no separate Service Master object.
Instead, both materials and services are maintained within a single master data structure known as the Item Master.
This Item Master captures:
- Physical materials
- Spare parts
- Consumables
- Non-stock items
- Services
The distinction between a material and a service is controlled through item-level attributes.
How Oracle differentiates Services from Materials
A service record in Oracle is essentially an Item Master record configured as non-inventory.
Key attributes include:
- Stockable = NO
→ Indicates the item is not physically stocked - Inventory Asset Value = NO
→ Ensures the service does not impact inventory valuation - Purchasing Attributes Enabled
→ Unit of Measure, supplier details, pricing, and procurement controls are maintained
Example Oracle Service Item
Attribute | Value |
Item Number | ITM-SVC-2045 |
Description | Annual Electrical Inspection Service |
Stockable | No |
Inventory Asset | No |
Primary UOM | EA |
Purchasing Enabled | Yes |
From a system perspective, Oracle treats services as:
“Items that can be purchased but not stocked.”
Implication of Oracle’s approach
Advantages
- Single master data table
- Simpler data model
- Uniform procurement handling
Challenges
- Services lack a dedicated schema
- Limited service-specific governance
- Greater risk of duplication
- Heavier dependency on naming standards
Because services and materials share the same master, strong governance and classification standards are essential in Oracle environments.
Service Master Configuration in Other ERPs
Microsoft Dynamics 365’s approach is similar to Oracle in that it does not use a separate “Services Master” object for basic procurement but relies on the Item Master coupled with specialized functional modules.
Infor LN, particularly with its strong roots in manufacturing and complex asset management, often has the most structured approach, similar to SAP, by dedicating specific master data structures within its relevant domains.
Read More
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 follows a model similar to Oracle.
It does not maintain a standalone Service Master for basic procurement.
Instead, services are created within the Item Master, typically using:
- Item Type = Service
- No inventory tracking
- Procurement attributes enabled
Example Dynamics Service Item
Field | Value |
Item Number | SRV-00128 |
Item Type | Service |
Inventory Tracking | Disabled |
UOM | Hour |
Procurement Enabled | Yes |
While Dynamics offers additional modules for service management, logistics, or field service, the base procurement record for a service still originates from the Item Master.
This approach works well for organizations with:
- Moderate service volumes
- Simpler procurement models
However, as service complexity increases (MRO, maintenance, contracts, multi-vendor services), governance becomes more difficult without a dedicated service data structure.
Service Master in Infor LN
Infor LN has one of the most structured approaches to Service Master Data, especially for manufacturing and asset-intensive industries.
Unlike Oracle or Dynamics, Infor LN provides dedicated service-oriented master data structures, similar to SAP.
Infor LN supports:
- Service types
- Standard service tasks
- Labor categories
- Skill definitions
- Service coverage models
- Maintenance and repair structures
Example Infor LN Service Data
Service Type | Example |
Preventive Maintenance | Annual Compressor Inspection |
Corrective Maintenance | Emergency Motor Repair |
Contract Service | AMC – Utilities Equipment |
Labor Category | Electrical Technician – Level 2 |
These service records integrate deeply with:
- Equipment master
- Maintenance planning
- Service contracts
- Warranty tracking
Because of this design, Infor LN is particularly strong in:
- Complex asset maintenance
- Aftermarket service management
- Equipment lifecycle tracking
Summary: How ERPs Handle Service Master Data
ERP | Service Master Approach |
SAP | Dedicated Service Master within MM module |
Oracle | Services maintained as non-stock items in Item Master |
Microsoft Dynamics | Service items within Item Master |
Infor LN | Structured service master objects integrated with maintenance domains |
Why this matters for Master Data Management
Because Service Master Data is structured differently across ERPs, organizations face challenges when:
- Running multiple ERP systems
- Migrating from legacy ERP to S/4HANA or Cloud
- Consolidating global service catalogs
- Performing enterprise-wide spend analytics
This is where Multi-Domain Master Data Management becomes critical – providing a harmonized service master layer that sits above ERP-specific data structures and enforces consistency, governance, and standardization across the enterprise.
Service Master Data Across Industries
Service Master Data represents all non-physical services that an organization procures from external parties. While the structure of a service master record remains largely consistent across enterprises, the nature, complexity, and volume of services vary significantly by industry.
Each industry maintains a distinct service catalog based on its operational model, regulatory environment, and dependency on external vendors.
Below is an industry-wise breakdown of how Service Master Data is used and what types of service records are typically maintained.
Manufacturing & Asset-Intensive Industries
In manufacturing and asset-intensive industries, service master data spans far beyond plant maintenance. It includes services consumed by production, engineering, quality, IT, supply chain, finance, HR, and compliance departments. As a result, manufacturing organizations typically maintain one of the largest and most complex service catalogs.
Types of service data captured
- Preventive and corrective maintenance services
- Equipment overhaul and refurbishment services
- Calibration, testing, and quality inspection services
- Production line installation and commissioning services
- Industrial engineering and process optimization services
- Automation, PLC, and MES support services
- Facility management, utilities, and housekeeping services
- Transportation and logistics services
- Environmental, safety, and statutory compliance services
- Professional services such as audit, legal, and consulting
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Centrifugal Pump Overhaul Service | EA | Mechanical Maintenance |
CNC Machine Calibration Service | EA | Quality & Calibration |
Production Line Commissioning | PROJECT | Manufacturing Support |
PLC Automation Support Service | DAY | Automation Services |
Utility System Preventive Maintenance | DAY | Facility Maintenance |
Internal Safety Audit | EA | HSE Compliance |
Finished Goods Transportation | TRIP | Logistics |
Legal Advisory Services | HOUR | Professional Services |
Standardized service master data enables accurate costing, asset lifecycle tracking, cross-department spend visibility, and integration with material, supplier, and asset master data.
Oil & Gas and Petrochemical Industry
In oil & gas and petrochemical organizations, service master data supports operational, engineering, safety, logistics, IT, compliance, and corporate functions across upstream, midstream, and downstream operations.
Types of service data captured
- Drilling, well intervention, and reservoir services
- Process engineering and technical consulting services
- Shutdown, turnaround, and maintenance services
- Inspection, testing, and certification services
- Offshore marine, aviation, and logistics services
- Environmental, safety, and risk consulting services
- Industrial automation and OT system services
- Security, surveillance, and access control services
- Legal, audit, and regulatory advisory services
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Directional Drilling Service | DAY | Drilling Operations |
Well Logging Services | JOB | Subsurface Services |
Turnaround Maintenance Support | DAY | Plant Shutdown |
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) | EA | Inspection Services |
Offshore Vessel Charter Service | DAY | Marine Logistics |
HAZOP Risk Assessment Study | EA | HSE Compliance |
SCADA System Support | MONTH | OT Services |
Offshore Security Services | MONTH | Security |
Legal Retainer Services | MONTH | Professional Services |
A governed service master is critical for safety traceability, regulatory audits, and cost governance in high-risk industrial environments.
Chemicals & Process Industries
Chemical and process manufacturing industries operate under strict safety, environmental, and regulatory frameworks. Service master data here supports operations, R&D, compliance, quality, logistics, and corporate services.
Types of service data captured
- Process plant maintenance and shutdown services
- Laboratory testing and chemical analysis services
- Environmental monitoring and emission testing services
- Safety audits and statutory inspections
- Process optimization and engineering consulting
- Waste treatment and hazardous material disposal services
- Packaging, transportation, and handling services
- ERP, LIMS, and manufacturing IT services
- Regulatory, legal, and compliance consulting services
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Reactor Preventive Maintenance | EA | Process Maintenance |
Chemical Sample Analysis | TEST | Laboratory Services |
Stack Emission Monitoring | EA | Environmental Compliance |
Process Safety Audit | EA | HSE Compliance |
Hazardous Waste Disposal Service | TON | Waste Management |
Chemical Transportation Service | TRIP | Logistics |
LIMS System Support | MONTH | IT Services |
Regulatory Compliance Advisory | HOUR | Professional Services |
Well-structured service masters ensure regulatory adherence, environmental reporting accuracy, and traceability of safety-critical services.
Power, Utilities & Infrastructure
Power and utility organizations rely on service master data across generation, transmission, distribution, IT, safety, regulatory, and customer operations.
Types of service data captured
- Power plant and grid maintenance services
- Equipment diagnostics and testing services
- Field inspection and fault restoration services
- Smart metering and AMI services
- Environmental and statutory compliance services
- Engineering and technical consulting services
- SCADA, monitoring, and IT support services
- Security, housekeeping, and facility services
- Audit and regulatory advisory services
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Transformer Oil Testing Service | EA | Electrical Testing |
Substation Preventive Maintenance | DAY | Asset Maintenance |
Transmission Line Patrol | KM | Field Services |
Smart Meter Calibration Service | EA | Metering |
Electrical Safety Compliance Audit | EA | Regulatory Compliance |
SCADA Monitoring Support | MONTH | Control Systems |
Power Plant Security Services | MONTH | Security |
Environmental Audit Services | EA | Sustainability |
Consistent service master data supports grid reliability, audit readiness, and transparent cost allocation.
Logistics & Warehousing
Logistics organizations manage service data across transportation, warehousing operations, compliance, IT systems, and commercial services.
Types of service data captured
- Road, rail, air, and ocean transportation services
- Freight forwarding and consolidation services
- Warehouse storage and handling services
- Packaging, labeling, and kitting services
- Customs clearance and trade documentation services
- Fleet maintenance and repair services
- Logistics platform and tracking system services
- Insurance, claims, and risk advisory services
- Professional and financial services
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Full Truck Load Transportation | TRIP | Logistics |
Warehouse Storage Service | PALLET/DAY | Warehousing |
Container Unloading Service | EA | Material Handling |
Export Customs Clearance | SHIPMENT | Trade Compliance |
Fleet Preventive Maintenance | EA | Fleet Services |
Logistics Platform Support | MONTH | IT Services |
Cargo Insurance Advisory | EA | Risk Services |
Financial Audit Services | EA | Professional Services |
A unified service master enables accurate freight billing, spend visibility, and supplier performance management.
IT & Software Industry
Legal, auditory and consulting services along with a brief description of their nature are also captured with reference to the law firm/independent solicitor in charge of fulfilling that service.
Legal and compliance functions also depend on external professional services.
Types of services captured
- Legal advisory services
- Litigation support
- Compliance audits
- Regulatory consulting
- Intellectual property services
Example Service Master Records
Service ID | Service Description | UoM | Category |
SVC-6001 | Corporate Legal Advisory Services | HOUR | Legal Services |
SVC-6002 | Regulatory Compliance Audit | EA | Compliance |
SVC-6003 | Contract Review & Vetting | EA | Legal Review |
These records are linked to:
- Law firms
- Independent consultants
- Regulatory agencies
They help organizations track legal spend, manage engagements, and maintain audit readiness.
Banking, Financial Services & Insurance (BFSI)
BFSI institutions manage service data across compliance, IT, audit, operations, and corporate governance functions.
Types of service data captured
- Internal and external audit services
- Risk, compliance, and regulatory consulting
- Core banking and application support services
- Cybersecurity and fraud monitoring services
- Data governance and privacy services
- Process re-engineering and advisory services
- Facility, security, and branch services
- Legal and professional services
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Internal Audit Services | EA | Audit |
Regulatory Compliance Advisory | HOUR | Risk Consulting |
Core Banking Support Services | MONTH | IT Operations |
Fraud Monitoring Services | MONTH | Security |
Data Privacy Assessment | EA | Compliance |
Process Improvement Consulting | DAY | Advisory |
Branch Security Services | MONTH | Facility Services |
Legal Retainer Services | MONTH | Professional Services |
Standardized service masters are essential for audit trails, regulatory transparency, and financial governance.
Construction & Infrastructure
Construction organizations rely on service master data to manage project execution, subcontracting, safety, logistics, and corporate services.
Types of service data captured
- Engineering, design, and consulting services
- Site survey and geotechnical services
- Equipment rental and commissioning services
- Construction supervision and project management
- Quality inspection and testing services
- Safety and statutory compliance services
- Project logistics and transportation services
- Contract, legal, and advisory services
Example Service Master Records
Service Description | UoM | Category |
Site Survey and Geotechnical Study | EA | Engineering Services |
Crane Rental Service | DAY | Equipment Services |
Construction Safety Audit | EA | HSE Compliance |
Project Material Transportation | TRIP | Logistics |
Construction Supervision Services | MONTH | Project Services |
Quality Inspection Services | EA | QA/QC |
Contract Advisory Services | HOUR | Legal Services |
A standardized service master ensures project cost transparency, contractual governance, and accurate vendor billing.
Common Challenges with Managing a Service Master
Service data management is a cornerstone of operational efficiency, particularly in industries that rely heavily on outsourced services or complex procurement networks. However, managing service data effectively is fraught with unique challenges.
Unlike material data, which deals with tangible items, service data is intangible, diverse, and often unstructured. These characteristics make it more difficult to classify, standardize, and manage effectively. Below, we explore the key challenges businesses face in managing service data and how these issues can impact operations.
Creating duplicate service records is rampant because it’s often easier for a buyer to create a new, slightly different entry than to search for the existing one. This fragments spend data across multiple service codes.
In many organizations, it is unclear who “owns” the Service Master Data. Unlike a material, which is clearly owned by a Material Master team or Engineering, service creation often defaults to individual buyers or department heads, leading to inconsistent formats.
Many services are created for a single, unique project. If these records are not retired or flagged as inactive after the project ends, the Service Master table becomes cluttered and difficult to search, increasing the risk of using obsolete codes.
While Services are also classified in official taxonomy standards like UNSPSC, the general consensus is that UNSPSC has historically been stronger and more detailed in capturing tangible goods than intangible services.
One can argue that this gap has steadily been closing but challenges remain due to the complexity inherent in-service contracts.
Service master records can quickly become outdated if they are not dynamically linked to their corresponding contracts (e.g., blanket purchase agreements).
The master record might indicate a service exists, but the contract containing the valid pricing or scope may have expired.
The lack of a Universal U-O-M is a known challenge in several Master Data domains, however, it is particularly pronounced in the case of a “Service Master”
While a material uses a standard unit (EA, KG), service UOMs are highly variable and “context-dependent”
A “day” of consulting is not the same as a “day” of heavy equipment rental. Inconsistency in the Unit of Measure (UOM) makes pricing and contract management extremely difficult.
Lack of Standardized Classification
One of the primary challenges in managing service data is the absence of consistent classification standards. Services, unlike materials, are often described differently by various stakeholders, leading to inconsistent entries in service master data.
Impact: This inconsistency hampers integration with enterprise systems like ERP and procurement platforms, complicating spends analysis and vendor comparisons.
Solution: Adopting globally recognized classification systems, such as UNSPSC, can help ensure uniformity and make data more accessible across departments.
Inconsistent and Incomplete Data
Service data often lacks the structured attributes found in material data, making it prone to errors and omissions. For example, incomplete service descriptions or missing pricing details can lead to inefficiencies in procurement and vendor management.
Impact: Incomplete data causes delays in service delivery, increases procurement costs, and creates challenges in decision-making.
Solution: Implementing data validation processes and mandatory data fields can help maintain data completeness and accuracy.
Difficulty in Quantifying Services
Unlike materials, which can be measured and tracked in units, services are qualitative in nature and often lack clear quantifiable metrics. This makes it challenging to assess the value and performance of services.
Impact: The inability to quantify services results in poor vendor performance tracking and difficulty in cost allocation.
Solution: Defining measurable service-level agreements (SLAs) and key performance indicators (KPIs) can help quantify and evaluate service quality.
Decentralized Data Management
Service data is often scattered across various departments, such as procurement, finance, and operations, with no centralized repository.
Impact: This decentralization leads to data duplication, discrepancies, and siloed information, which undermines collaboration and consistency.
Solution: Investing in a centralized master data management (MDM) system allows for better data governance and ensures that service data remains consistent and accessible across the organization.
High Complexity and Diversity of Services
Services vary significantly across industries and vendors, from one-time consultancy engagements to recurring maintenance contracts. This diversity adds complexity to service master data management.
Impact: Managing such varied data without proper categorization leads to inefficiencies in procurement and makes reporting more cumbersome.
Solution: Categorizing services into predefined hierarchies and leveraging advanced classification tools can simplify data management.
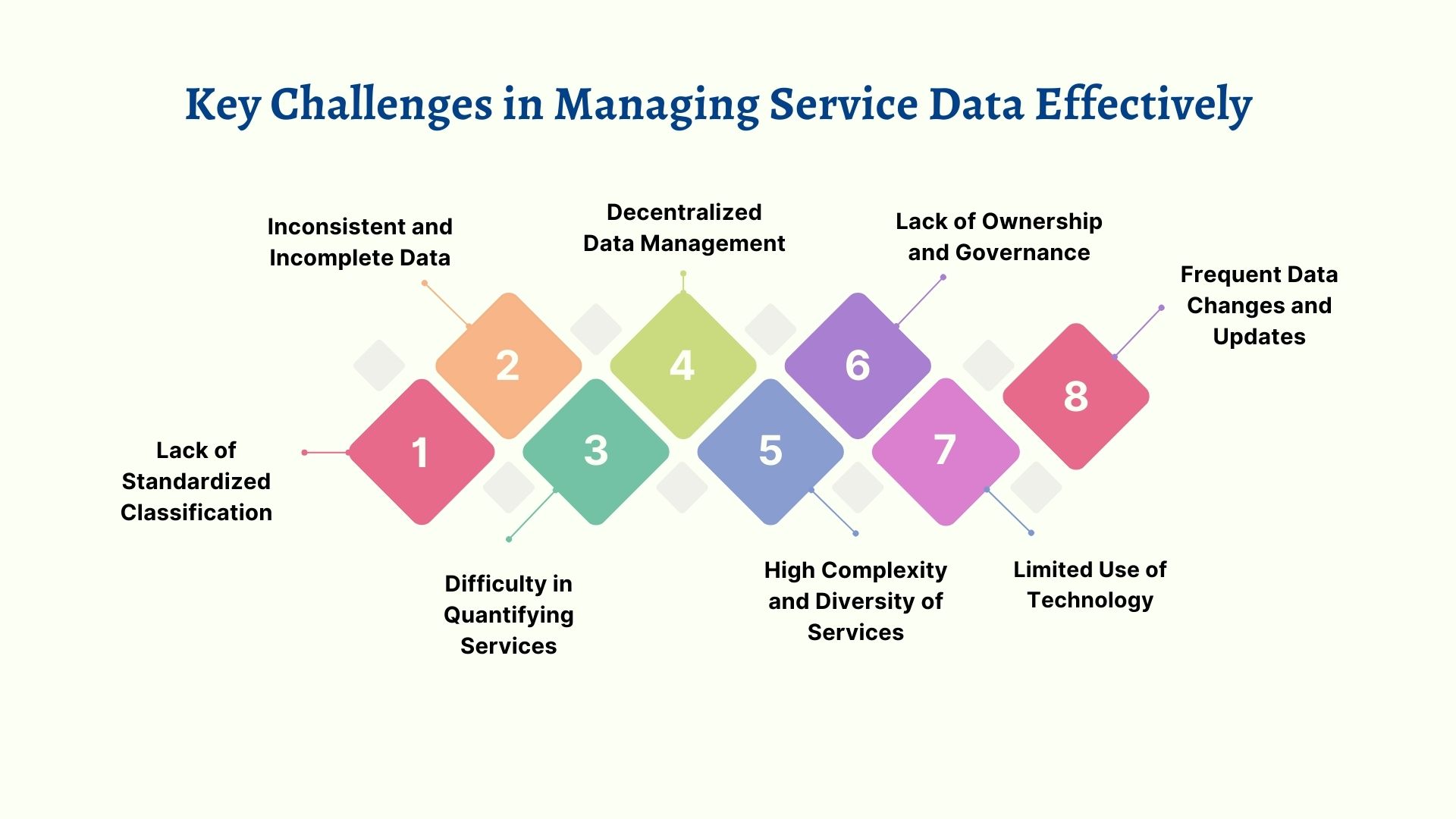
Lack of Ownership and Governance
Without clear accountability, service data management often falls through the cracks. Departments may create duplicate or inconsistent entries due to the lack of defined ownership and governance policies.
Impact: Poor governance results in data errors, audit failures, and reduced confidence in service data quality.
Solution: Establishing a governance framework that defines roles, responsibilities, and approval workflows ensures accountability and adherence to data quality standards.
Limited Use of Technology
Many organizations still rely on manual processes or outdated tools for managing service data, which are neither scalable nor efficient.
Impact: Limited technological adoption leads to slow data processing, human errors, and an inability to adapt to changing business needs.
Solution: Leveraging advanced MDM platforms equipped with AI and automation capabilities can enhance data accuracy, deduplication, and scalability.
Frequent Data Changes and Updates
Service data often requires frequent updates due to changing vendor agreements, pricing structures, or regulatory requirements.
Impact: Without proper version control and monitoring mechanisms, these changes can result in outdated or incorrect data being used in critical processes.
Solution: Regular data audits and automated update mechanisms help maintain up-to-date and accurate service data.
How a Service Master is Configured in ERP
Multi-Domain Master Data Management & Service Master
Verdantis’ flagship master data management software supports “Services” as and object with configured integrations directly into widely used ERPs.
To overcome some of the challenges associated with “Services” master as discussed above, here’s how Verdantis MDM Suite empowers maintenance, asset management, reliability and supply chain teams with up-to-date and reliable service master records.
Real-time Sync with Service Contracts
As mentioned previously, service records get stale over time as the engagement with the vendor and the corresponding service contract changes.
Lackadaisical data governance practices often mean that these changes are not captured in the data records.
To counter these challenges, the Service Master Object in Verdantis’ MDM suite can be configured to;
- Run a Batch Analysis: Embedded AI agents in the MDM suite, like Auto Doc AI, can be configured to match the clauses in any given service contract at regular intervals, if a mismatch is detected, a workflow can be configured that will enforce an edit to the data record and complete it based on the master data governance standard that has been defined.
This sync is a governance-first approach to master data, that ensures that one of the most tedious challenges in service MDM, that is duplication, is minimized and
AI-Driven U-O-M Analysis
- Service contracts are complex and can be billed based on several measures/milestones – Man hours, rental duration, fixed scope, milestone completion etc.
Verdantis’ document processing software is industry-trained on several service contracts and since these models are “Context-aware”, it’s possible to use Agentic AI frameworks to auto create the units of measure, in-line with the service contract and add the values in the service master data record.
AI-Driven Classification & Descriptions
Based on the accepted classification standards, service records and it’s nature can automatically detected, codified and updated into the system with a human-in-the-loop AI workflow
This automates what is probably one of the most painful challenges in service MDM, that is, duplication and unstructured descriptions.
Key Steps in Service Data Management
Service data management is a crucial component of any organization’s data governance framework. With services playing a central role in modern business operations, effective service data management can lead to improved procurement practices, enhanced compliance, and operational efficiency. The following are the key steps in the service data management process, from data collection to validation.
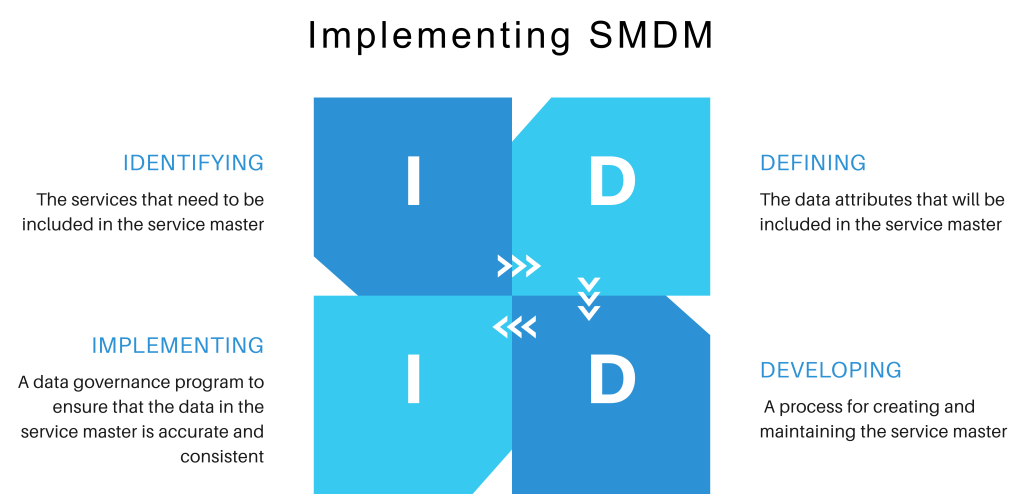
Data Collection: Sources of Service Data
The first step in effective service data management is the collection of service-related information. This involves gathering data from multiple internal and external sources to ensure a comprehensive and accurate record of all services provided or received by the organization.
Common sources of service data include:
Contracts: These contain detailed descriptions of services, pricing structures, service level agreements (SLAs), and terms and conditions. Contracts serve as a primary reference for data related to the scope, duration, and cost of services.
Invoices: Invoices provide critical data on service usage, pricing, discounts, payment terms, and dates of service delivery. They are vital for tracking the financial aspect of service procurement.
Procurement Systems: These systems contain records of service purchases, including vendor information, service specifications, quantities, and payment history. They are key sources for tracking ongoing or recurring services.
Service Requests and Work Orders: In organizations with maintenance or operations teams, work orders and service requests serve as sources of real-time service data, documenting requests for specific services and their status.
Collecting service data from multiple systems helps create a comprehensive and accurate picture of the services an organization uses, ensuring that the data reflects the latest transactions and agreements.
Classification: Grouping Services Using Appropriate Taxonomies
Once service data is collected, the next crucial step is classification—grouping services into categories that can be easily managed, compared, and analysed. Effective classification helps streamline procurement, improve spend analysis, and ensure that services are aligned with business objectives.
Common classification systems include:
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code): This global classification standard categorizes services into segments, families, classes, and commodities, ensuring consistency across procurement systems and markets. For example, consulting services could be categorized under the segment “Professional Services,” with further subcategories for specific types of consulting (e.g., IT consulting).
E-class: This system is widely used in Europe and is particularly helpful for industries like manufacturing and engineering. It allows for more granular classification of services, with an emphasis on attributes that define the nature of the service.
We will explore UNSPSC and E-class topic in greater detail as we progress through this blog.
Custom Taxonomies: Some organizations may develop their own custom classification systems based on internal requirements or industry-specific needs.
Proper classification helps improve visibility and transparency into service-related spending and allows businesses to quickly assess service performance across categories.
Validation: Ensuring Service Descriptions, Units of Measure, and Prices Align with Business Requirements
After collecting and classifying the service data, the next step is validation—ensuring that the data aligns with business requirements and is accurate, complete, and up to date. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the data and minimizing errors or discrepancies that could impact decision-making.
Key validation activities include:
Service Descriptions: Ensuring that service descriptions are accurate, clear, and consistent with internal and vendor-specific documentation. The description should match the agreed scope of work and meet the organization’s quality standards.
Units of Measure (UOM): Verifying that the units of measure (e.g., hours, pieces, contracts) are consistent with business standards and are appropriate for the type of service being provided. For example, if a service is billed by hours, the UOM should clearly reflect this to avoid billing disputes.
Pricing and Terms: Ensuring that pricing information, payment terms, and discounts are consistent with contracts and agreements. Regularly validating service pricing is especially important in long-term contracts where price adjustments or service additions may occur.
Compliance Checks: Ensuring that services comply with industry regulations, internal policies, and quality standards. This is critical in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, where non-compliance could lead to legal or financial consequences.
Validating service data is an ongoing process that helps ensure that services are being provided and paid for correctly, improving financial control and reducing the risk of errors and disputes.
SERVICE MASTER DATA- CLASSIFICATION
Integrations with other ERP modules
A service master data in and of by itself may not yield much in the way efficiency, the benefits of a reliable service master comes through after integrations with other ERP modules, namely;
An asset BOM is simply a hierarchical, structured list of all the materials and components required to build, maintain, and repair a specific physical asset (e.g., a pump, a production machine, or a vehicle).
Service contracts specific to the given maintenance task may require several additional spare parts or consumables in order to carry out the execution smoothly.
With an integration with Asset BOMs, this tracking can be made quite simple, straightforward, traceable, ensuring a holistic process.
- Digital Work Orders
A work order is a list of tasks, technical specifications and detailed scope of work that is created before a technician begins corrective or preventive maintenance work for a given piece of machinery.
External service contracts can also be linked with digital work orders to track their completion.
- Plant Maintenance OR Enterprise Asset Management (PM/EAM)
Integrating Service Master Data with Plant Maintenance (PM) or Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) modules creates a seamless link between maintenance planning and external procurement.
While PM focuses on the “what” and “when” of a repair, Service Master Data (along with other integrated data domains) provides the “who” and “how much” for services performed by external contractors.
Integration Touchpoints in the PM Module
Apart from Work Orders (as Discussed above) which is also managed in the PM module, these are the additional workflows where Service Master can be integrated.
Service Entry Sheets
Once the contractor completes the work, the maintenance team confirms the task against the work order. This triggers the creation of a Service Entry Sheet, which acts as the “Goods Receipt” for intangible services, ensuring the maintenance costs are accurately posted to the asset
Maintenance Task Lists
Frequently recurring external services (like annual elevator inspections) can be stored in a General Task List. By embedding Service Master data here, you can automate the procurement details every time a preventive maintenance plan triggers a new order.
It is important to note that only companies with a certain level of operational maturity put their Service Master to use through these deep integrations, and one of the pre-requisites for this a multi-domain master data integration that will ensure data and context is collated from multiple sources.
Integrations with Master Data Modules
- Materials Master Data
The materials master data also generally exists in the MM module (in SAP) and an equivalent module in other ERP systems.
This master data tracks the various direct and indirect materials that have been procured and that are in the process of being procured.
Direct materials are simply the raw materials and input items that go into the manufacturing or distribution process.
Indirect materials are the spare parts, consumables, admin materials, stationary etc.
An integration with material master records will enable trackability across service activities along with materials consumed for each service bucket.
This integration can be used for refining operational procedures, analysis and ensure optimization across MRO Inventories
- Fixed Asset Master Data
Also interchangeably referred to as equipment master, this master data domain captures the core data fields pertaining to every fixed asset. Excellence in MRO Production operations dictates that service master data entries, especially those undertaken for equipment upkeep, should be integrated with the fixed assets.
- Supplier Master Data
A supplier master data is the reference data pertaining to vendors and suppliers used org-wide along with static details pertaining to their contact information, Tax Identification and other details.
A more holistic resource on supplier master data and how software solutions can be leveraged for effective vendor MDM is captured here.
The data records in a supplier master includes suppliers of tangible materials and services as well so integration between services and supplier master data is non-negotiable for enterprise teams looking to drive process improvements.
Use Cases for Effective Service Master Data Management
- Manufacturing – Predictive Maintenance at Scale (Global Equipment Manufacturer)
A global industrial equipment manufacturer manages 5,000+ equipment assets across 12 plants, contracting preventive maintenance services annually for pumps, motors, and control systems. Service Master records codify each maintenance type (quarterly inspections, lubrication, component replacement) linked to asset BOMs using UNSPSC class 73152101. Integration with the PM (Plant Maintenance) module ensures:
Automatic service entry sheet (SES) generation when PM work orders complete, reducing manual invoice reconciliation by 500+ working hours annually per site
Real-time visibility into service spend by asset class, enabling cross-plant price negotiations and achieving 12-15% annual cost reduction
SLA tracking and vendor performance scoring tied to service master specifications
Post-implementation, the company achieved matching accuracy improvement from 30-40% to 80%, with cost per record reduction to approximately 8 cents (infrastructure + service costs).
- Oil & Gas – Contract Management at Enterprise Scale
A Fortune 20 energy operator manages 180+ service vendors providing drilling fluids, well maintenance, inspection, and logistics services. It processes 80–100 service catalogs daily with strict timelines (50–200 general catalogs/day; 2–5 days per complex Oil Field Services catalog). Service Master standardization with UNSPSC and internal Material Group Codes (e.g., UNSPSC 71121503 for Oil Field Services) ensures:
Unified sourcing strategy across disparate OFS service categories, reducing maverick spend by 18%
Compliance with regulatory documentation (HSE, environmental), audit-ready SES records with 100% traceability
10% reduction in annual MRO spend (USD $8-12M savings annually for large operators) through consolidated contracts and duplicate elimination
The company implemented batch deduplication across 45,000+ service records, reducing duplicate spend leakage from 6.2% to 0.8% within 4 months.
Future Trends in Service Data Management
As businesses continue to evolve in a digital-first world, service data management is undergoing a transformation driven by emerging technologies and automation. The ability to manage, standardize, and validate service data efficiently is becoming increasingly critical for organizations looking to optimize procurement, improve compliance, and enhance decision-making. Below are two key trends shaping the future of service data management.
Adoption of AI for Service Data Standardization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way organizations classify, validate, and manage service data. AI-driven automation helps businesses overcome common challenges such as inconsistent service descriptions, duplicate records, and manual classification errors.
Key Benefits of AI in Service Data Management:
Automated Classification: AI algorithms can map service descriptions to standard taxonomies like UNSPSC and E-class, ensuring consistency across systems.
Duplicate Detection & Data Cleansing: Machine learning models can identify redundant or conflicting service entries and suggest corrections, leading to higher data accuracy and reduced procurement inefficiencies.
Context-Aware Data Enrichment: AI can analyse historical service transactions and recommend additional metadata, such as pricing benchmarks or vendor ratings, to enhance decision-making.
For example, AI-powered tools can automatically classify a consulting service under UNSPSC Code 80101500 (Business and Corporate Management Consultation Services), reducing manual effort and improving procurement transparency.
Real-Time Data Updates and Validation in the Cloud
With businesses increasingly adopting cloud-based procurement and ERP systems, real-time service data management is becoming a necessity. Cloud platforms enable seamless data synchronization across multiple departments, ensuring consistent and up-to-date service records.
Key Advantages of Cloud-Based Service Data Management
Instant Data Updates: Changes to service descriptions, pricing, and contract details can be reflected across all systems in real time, reducing errors and misalignment.
Automated Data Validation: Cloud platforms can integrate with external data sources and AI-driven validation engines to check for inconsistencies, missing fields, or incorrect classifications.
Scalability & Flexibility: Cloud solutions can handle large volumes of service data without performance degradation, making them ideal for growing enterprises with expanding service portfolios.
For instance, a global company using a cloud-based MDM (Master Data Management) system can instantly update service rates across regional offices, ensuring compliance with contractual agreements and enhancing financial forecasting accuracy.
Let’s look at some benefits of implementing a Services Master:
A single centralized source of truth
An integrated SMDM solution ensures all cleansed and standardized master data is stored at a single location in the cloud, easily accessible from across locations. It further leads to improved cross-plant collaboration and real-time visibility into any updates to the master data.
Consistent, structured descriptions
An advanced services master ensures corporate wide consistent, structured, reliable descriptions and services linked to global classification standards like UNSPSC.
Process and performance improvement
With a centralized, cleansed services master, companies have access to data at their fingertips. This data doesn’t just help in analysing performance and making corporate decisions but also helps in eliminating duplicates and enables on-time maintenance routines. Automated workflows and process streamlining helps clear bottlenecks and delays and ensures smooth and seamless process flow and improved ERP performance.
Advanced search capabilities
With multiple search features like ‘free-text search’, ‘search by category’, etc., finding the necessary services data with the help of just a keyword, a category, or an attribute becomes easy and quick. This improves visibility, reduces unnecessary purchases, and gives a granular view of the entire services master data.
Improved data security
An SMDM can ensure a heightened level of data security with user authentication role-based data access to only authorized personnel. Access logs can provide an audit trail with time stamps and improve individual accountability. With insecure activities getting flagged automatically, any unauthorized breach of data is contained.
Digitization and industrial revolution 4.0 have reiterated the importance of good quality data and the repercussions of depending on sub-standard, unreliable data. With data influencing strategic decisions, improving processes and productivity, and reducing costs, a cleansed, standardized services master can come with a host of opportunities and benefits for an organization. Be an early adopter of services master data management and get an edge over your competition!
Conclusion
Service master data management is a critical component of modern business operations, enabling organizations to achieve data consistency, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. By implementing standardized classification systems (UNSPSC, E-class), leveraging AI-driven automation, and adopting cloud-based MDM solutions, businesses can significantly improve their procurement efficiency, optimize costs, and ensure strategic agility.
Failure to manage service master data effectively can lead to severe consequences, including procurement inefficiencies, financial misstatements, compliance risks, and missed cost-saving opportunities. Standardization and rigorous governance frameworks are essential for preventing these risks and ensuring data integrity.
How Verdantis Can Help
Verdantis, specializes in MRO lifecycle and asset management software solutions that enable organizations to build excellence in asset reliability, eliminate downtime, and drive maintenance efficiency. With powerful tools like MRO360, Harmonize and Integrity to help organizations manage and cleanse their service master data. These solutions provide:
Automated Data Harmonization: Ensuring consistency by standardizing service descriptions, classifications, and attributes.
Data Cleansing & Enrichment: Identifying duplicates, correcting errors, and enriching service data with missing attributes.
AI-Powered Classification: Leveraging AI to map services to global standards like UNSPSC and E-class automatically.
Seamless Integration: Enabling real-time data synchronization across ERP, procurement, and analytics platforms.
Governance & Compliance Support: Implementing workflows that maintain data integrity and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
By leveraging Verdantis’ cutting-edge technology, businesses can eliminate inefficiencies, optimize procurement processes, and enhance overall data quality, making service master data management a strategic asset rather than a challenge.
Investing in the right tools and methodologies ensures that organizations remain competitive and well-equipped to navigate the complexities of modern procurement and service management.





